This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
peer-reviewed publication
trusted source
proofread
New guidance published to aid researchers evaluating surgical robots
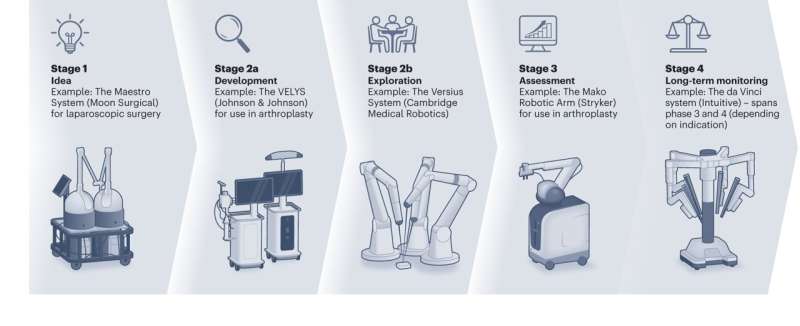
Surgical robotics are among the most complex devices entering health care, but how should we evaluate them? Published in Nature Medicine, the Idea, Development, Exploration, Assessment and Long-term monitoring (IDEAL) Robotics Colloquium outlines the latest guidance to aid researchers evaluating surgical robots. The paper is titled, "The IDEAL framework for surgical robotics: development, comparative evaluation and long-term monitoring."
Surgical robots are poised to significantly alter the health care landscape, with expansion of the field of robotics increasingly permeating health systems. This is an exciting time for both patients and surgeons, but is not without risk.
Lessons from the past showcase the harms of innovating without evaluating, and as the diffusion of surgical robots increases, thoughtful and robust evaluation methods must be established.
While they pose the same traditional challenges seen when evaluating medical devices, they are among the most complex systems entering contemporary health systems, and are, by their nature, a disruptive innovation, obligating major changes in the way work is done and in the business model of surgery. This warrants bespoke analysis and careful evaluation.
Led by Mr. Hani Marcus (National Hospital for Neurology and Neurosurgery, and UCL Queen Square Institute of Neurology), Dr. Pedro Ramirez (Houston Methodist Hospital Neal Cancer Center) and Professor Peter McCulloch (Nuffield Department of Surgical Sciences, University of Oxford), the IDEAL Robotics Colloquium affords researchers and innovators recommendations to consider when evaluating surgical robots, structured according to the IDEAL Stages: "Preclinical Development and Early Clinical Evaluation" (IDEAL Stages 0–2a), "Comparative Evaluation" (IDEAL Stages 2b–3) and the "Long-term Monitoring and Technological Evolution" (IDEAL Stage 4).
This means guidance is provided through the life cycle of a surgical robot.
Surgical robots present novel challenges for evaluation. The paper tackles these challenges by presenting the IDEAL stages through four key perspectives: the device itself, the clinician using the robot, the patient receiving treatment and the wider health system it is entering.
"This paper is an important milestone in the maturation of surgical robotics research, bringing key perspectives together to improve how surgical robots are evaluated," said Professor McCulloch.
From the device perspective, the team found that the integration of artificial intelligence and increasing autonomy of robotic systems pose particular challenges. Current evaluation methods are unlikely to keep up with these rapidly evolving systems, requiring innovative, new approaches.
For clinicians, claims of their ergonomic benefit require validation, and the learning curves associated with their safe use must be considered.
For patients, new ethical challenges are introduced relating to informed consent and accountability, among other issues including patient acceptability and trust of autonomous systems.
When thinking about the health systems, the financial cost needs to be taken into consideration. Robots are expensive, meaning investment of scarce resources must be justified. There are also concerns about their carbon footprint or environmental impact, meaning this should be measured. Both examples highlight why robots must be considered in the context of wider global health needs.
The challenges are broad, and the multiple facets to be considered emphasize the complexity of these systems. While more work is needed, the hope is that the IDEAL guidelines will aid the advancement of robotics research, and therefore improved patient care.
More information: Hani J. Marcus et al, The IDEAL framework for surgical robotics: development, comparative evaluation and long-term monitoring, Nature Medicine (2024). DOI: 10.1038/s41591-023-02732-7