This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
peer-reviewed publication
reputable news agency
proofread
USPSTF: Evidence lacking for screening for speech and language delays
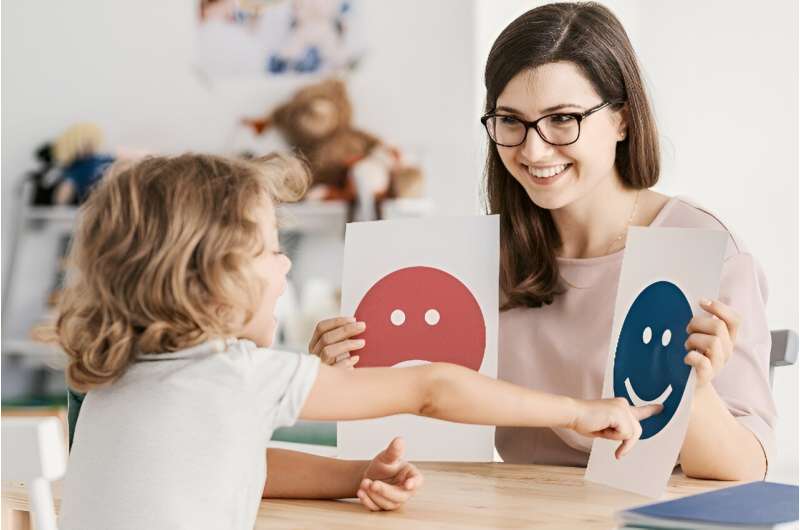

The U.S. Preventive Services Task Force (USPSTF) concludes that the evidence is currently inadequate for recommending primary care screening for speech and language delay and disorders among asymptomatic children aged 5 years and younger. These findings form the basis of a final recommendation statement published in the Jan. 23/30 issue of the Journal of the American Medical Association.
Cynthia Feltner, M.D., M.P.H., from RTI International-University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill Evidence-based Practice Center, and colleagues reviewed the evidence on screening for speech and language delay or disorders in children aged 5 years or younger to inform the USPSTF. Thirty-eight studies from 41 articles were included, with 9,006 participants. The researchers found that none of the studies assessed the direct benefits of screening versus no screening. Consistently high sensitivity and specificity were found in three studies assessing parent-reported tools for expressive language skills. There was wide variation noted in the accuracy of other screening tools. The benefit was found for different measures of expressive language skills in two randomized controlled trials evaluating relatively intensive parental group training interventions; no difference was seen for any outcomes in one trial assessing a less intensive intervention.
Based on these findings, the USPSTF concludes that the current evidence is inadequate for assessing the balance of benefits and harms of screening for speech and language delay and disorders among children without signs or symptoms or parent/caregiver-reported concerns (I statement).
"In the absence of evidence, health care professionals should use their judgment when deciding whether or not to screen children who are not showing signs of speech and language delay and disorders," USPSTF member Li LI, M.D., Ph.D., M.P.H., from the University of Virginia School of Medicine in Charlottesville, said in a statement.
More information: Cynthia Feltner et al, Screening for Speech and Language Delay and Disorders in Children 5 Years or Younger, JAMA (2024). DOI: 10.1001/jama.2023.24647
Screening for Speech and Language Delay and Disorders in Children, JAMA (2024). DOI: 10.1001/jama.2023.26952
Marisha L. Speights et al, Recommendations for Speech and Language Screenings, JAMA (2024). DOI: 10.1001/jama.2023.26817
Copyright © 2024 HealthDay. All rights reserved.