This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
proofread
Impact of onset time, number, type, and sequence of extrahepatic organ failure on prognosis of liver failure
The impact of the characteristics of extrahepatic organ failure (EHOF) including the onset time, number, type, and sequence on the prognosis of acute-on-chronic liver failure (ACLF) patients remains unknown. This study aimed to identify the association between the characteristics of EHOF and the prognosis of ACLF patients.
ACLF subjects enrolled at six hospitals in China were included in the analysis. The risk of mortality based on the characteristics of EHOF was evaluated. Survival of study groups was compared by Kaplan–Meier analysis and log-rank tests.
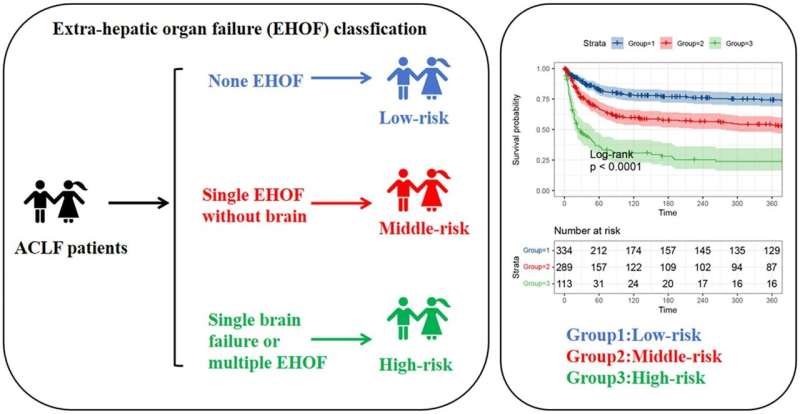
A total of 736 patients with ACLF were included. EHOF was observed in 402 patients (54.6%), of which 295 (73.4%) developed single EHOF (SEHOF) and 107 (26.6%) developed multiple EHOF (MEHOF). The most commonly observed EHOF was coagulation failure (47.0%), followed by renal (13.0%), brain (4.9%), respiratory (4.3%), and circulatory (2.3%) failure. Survival analysis found that MEHOF or SEHOF patients with brain failure had a worse prognosis.
However, no significant outcome was found in the analysis of the effect of onset time and sequence of failed organs on prognosis. Patients were further divided into three risk subgroups by the EHOF characteristics. Kaplan–Meier analysis showed that risk stratification resulted in the differentiation of patients with different risks of mortality both in the training and validation cohorts.
The mortality of ACLF patients was determined by the number and type, but not the onset time and sequence of EHOF. Risk stratification applicable to clinical practice was established.
The study is published in the Journal of Clinical and Translational Hepatology.
More information: Shaotian Qiu et al, Impact of Onset Time, Number, Type, and Sequence of Extrahepatic Organ Failure on Prognosis of Acute-on-chronic Liver Failure, Journal of Clinical and Translational Hepatology (2024). DOI: 10.14218/JCTH.2023.00379