This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
reputable news agency
proofread
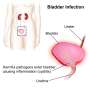
Obstructive sleep apnea linked to bladder pain / interstitial cystitis

Obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) seems to be associated with bladder pain syndrome/interstitial cystitis (BPS/IC) in women, according to a study published online Dec. 26 in Sleep and Breathing.
İbrahim Güven Çoşğun and Abdullah Gürel, from Afyonkarahisar Health Sciences University Medical Faculty in Turkey, compared the frequency of BPS/IC in 46 women diagnosed with OSA and 46 control women without OSA. Participants completed the Berlin Questionnaire, Epworth Sleepiness Scale (ESS), Interstitial Cystitis Symptom Index (ICSI), and the Interstitial Cystitis Problem Index (ICPI).
The researchers found no significant difference in age and body mass index between the women with OSA and control groups. Women with OSA had greater ESS than controls. The median ICSI was 8 and 5 in women with OSA and controls, respectively, and the median ICPI was 7 and 6, respectively.
"The results of this study demonstrated that BPS/IC symptoms and associated problems were seen more often in women at risk for OSA than in women at low risk of OSA," the authors write. "The positivity of the ESS was determined at a higher rate in the OSA group than in the control group."
More information: İbrahim Güven Çoşğun et al, Obstructive sleep apnea and bladder pain syndrome/interstitial cystitis in women, Sleep and Breathing (2023). DOI: 10.1007/s11325-023-02967-1
Copyright © 2024 HealthDay. All rights reserved.