This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
peer-reviewed publication
trusted source
proofread
First Nations patients leave ED without completing treatment more often than comparable non–First Nations patients

First Nations patients in Alberta leave emergency departments (EDs) without completing treatment more often than comparable non–First Nations patients, due in part to anti-Indigenous racism expressed by providers, found new research published in Canadian Medical Association Journal.
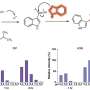
Higher proportions of incomplete ED care for First Nations patients compared with non–First Nations patients occurred even in cases of serious diagnosis, and were found across all parts of Alberta. Provincially, 6.8% of First Nations visits end without completing care, compared with 3.7% of non–First Nations visits.
Results from sharing circles with First Nations patients, and interviews with health care providers, show that racism and stereotyping are a reason First Nations patients leave care, which members from Alberta's white majority do not face. The study also identified that patient–provider communication issues, transportation barriers, long wait times, and perceptions of being made to wait longer than others were additional reasons why First Nations patients leave EDs.
Leaving without completing care matters because it delays needed treatment and interrupts care journeys. About 1 in 20 patients in the study required hospitalization within 72 hours of leaving. We do not know what proportion of patients may miss needed care entirely, because they do not return to the ED.
The work was conducted with the Alberta First Nations Information Governance Centre and involved 7 other First Nations organizations.
"There are multiple factors that influence the decision to leave the emergency department without being seen. Some of these include how First Nations [patients] are treated while waiting to be seen, such as minimizing and dismissing the urgency of presenting symptoms, feeling unsafe and the use of inappropriate language directed at them while in the emergency department," explains Lea Bill, RN, executive director of the Alberta First Nations Information Governance Centre.
"Although leaving care seems like a purely personal decision, more First Nations patients are making that decision than non–First Nations patients. This shows that those personal decisions are actually driven by overarching social factors and health system inequities," notes Patrick McLane, Ph.D., Department of Emergency Medicine, University of Alberta, Edmonton, Alberta.
Higher rates of First Nations patients leaving without completing care is of immediate concern as "crowding continues to worsen in emergency departments across Canada, and the proportion of patients leaving emergency department care has risen in several jurisdictions," the authors write.
The authors hope that study findings will encourage EDs to work with local First Nations to find ways to reduce disproportionate premature departures from care.
More information: Leaving emergency departments without completing treatment among First Nations and non–First Nations patients in Alberta: a mixed-methods study, Canadian Medical Association Journal (2024). DOI: 10.1503/cmaj.231019.