This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
peer-reviewed publication
trusted source
proofread
New SPECT/CT technique shows impressive biomarker identification, offers increased access for prostate cancer patients
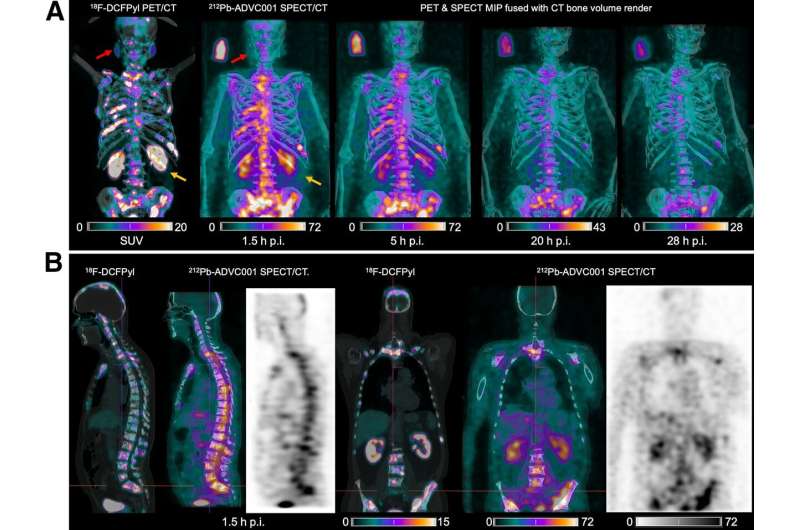
A novel SPECT/CT acquisition method can accurately detect radiopharmaceutical biodistribution in a convenient manner for prostate cancer patients, opening the door for more personalized treatment. Utilizing lead-212 (212Pb), the new imaging technique has the potential to change practice and increase access for patients around the world. The first-in-human images from this method are published in the Journal of Nuclear Medicine.
There is significant interest in the development of 212Pb-PSMA–based targeted alpha therapy (TAT) for patients with metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer. However, 212Pb is a challenging isotope to image because of the high-energy gamma rays generate significant scatter.
"The ability to acquire imaging of an alpha-emitter with a standard SPECT camera and standard collimator within a convenient acquisition time for the patient could provide more precision in how we treat patients with prostate cancer, and patients with other cancers, in the future. Confirming the presence of the drug in the target is important because it serves as a quality assurance and can be used to derive an understanding of the biodistribution and pharmacokinetics of the drug," said Stephen Rose, PhD, head of Translational Medicine and Clinical Science at AdvanCell.
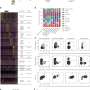
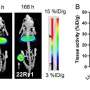
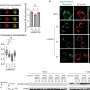
In the study, researchers administered 60 MBq of 212Pb-ADVC001 to a 73-year-old man with metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer. SPECT/CT imaging occurred at 1.5, 5, 20, and 28 hours after infusion.
Representative 212Pb SPECT/CT images showed rapid tumor uptake of 212Pb-ADVC001 in agreement with tumor burden shown on the pretreatment 18F-DCFPyl PET/CT images. Images acquired after 20 hours showed persistent tumor uptake despite low counts due to 212Pb decay.
"In the future, this imaging technique can help to streamline the drug development process, driving conviction in the agents we bring to larger scale trials. In addition, the ability to image 212Pb with a standard SPECT camera in a relatively short timeframe means that 212Pb is a true theranostic alpha-emitter and could be a valuable in selecting patients for targeted alpha-therapies," said Rose
He continued, "What's more, access to PET imaging is a bottleneck, in the United States and globally. SPECT cameras are more widely available and may address this critical issue, as SPECT imaging can be used for patient selection, therapy decision making, and guiding adaptive dosing strategies based on changes of target expression and tumor volume during treatment."
More information: Matthew R. Griffiths et al, First-in-Human212Pb-PSMA–Targeted α-Therapy SPECT/CT Imaging in a Patient with Metastatic Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer, Journal of Nuclear Medicine (2024). DOI: 10.2967/jnumed.123.267189