This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
peer-reviewed publication
trusted source
proofread
First seizure clinics reduce the need for future health care, researchers find
Clinics specializing in first seizures reduce the need for patients to present at emergency departments or be admitted to hospital later, Monash University-led research has found.
Published in JAMA Neurology, the study analyzed patients who attended first seizure clinics (FSCs) at two major Melbourne public hospitals, The Alfred and the Royal Melbourne Hospital (RMH).
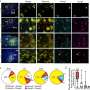
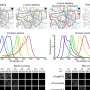
Timely attendance, particularly within 14 days of the seizure, was associated with reduced subsequent all-cause emergency presentations and all-cause hospital admission. Later hospital admissions were reduced by about 25%.
First author Dr. Yingtong Li, an adjunct research associate with the Department of Neuroscience in Monash University's School of Translational Medicine, said first seizure clinics were effective, and equitable access could offer substantial benefits to patients and health care systems.
"The findings show that early intervention in patients with seizures, when delivered through first seizure clinics, is highly effective and has the potential to change the trajectory of patients' subsequent health, through the lens of their health care utilization," Dr. Li said.
"In Australia, acute seizure care is estimated to cost AU$340 million annually. Our results suggest that approximately one-quarter of this (AU$85 million annually) could possibly be avoided if all patients were able to attend a first seizure clinic soon after their first event, accessing prompt, specialist care."
First seizure clinics were pioneered in Perth in 1990, established in Melbourne in 1994 and now serve several cities in Australia, the U.S., U.K. and Canada. They aim to deliver prompt specialist care to first-time seizure patients.
The clinics offer prompt access to clinical assessment and investigations such as electroencephalography (EEG) and neuroimaging. If appropriate, diagnosed patients take antiseizure medications and may be referred to their GP or neurologist.
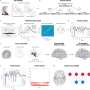
Other studies have demonstrated that first seizure clinics reduce time to diagnosis and treatment, but they have been limited in sample size and follow-up duration. The new record-linkage retrospective study aimed to identify whether clinic attendance improved long-term outcomes and reasons people may not attend the clinics.
The research covered 9,392 patients with a mean age at referral of 59.7 years, and found that clinic attendance, particularly early attendance, was associated with reduced rates of subsequent hospital use.
The authors found that patients benefited from early intervention. However, while international guidelines recommend neurologist review within two weeks, wait times can exceed this target, and such delays are associated with detrimental outcomes.
Senior author Dr. Emma Foster, a neurologist, co-head of Alfred Health's First Seizure Clinic and a Monash University School of Translational Medicine researcher, said the findings were exciting.
"There are some really important future research directions that follow on from this," Dr. Foster said. "Firstly, these clinics are resource intensive and only located in a handful of hospitals across Australia.
"Detailed health economic analyses are needed to understand if they are a cost-effective intervention. If yes, that would support their widespread implementation both in Australia and internationally.
"Secondly, this pilot study shows that attending First Seizure Clinic within 14 days of being referred significantly reduces the chance of future hospital attendances. Future studies need to identify and minimize the various barriers to First Seizure Clinic attendance across our community.
"Finally, health care utilization is just one of the impacts of first seizures. Future research should consider the personal impact of first seizures on people's mood, work, and quality of life. This may raise awareness and perhaps support interventions to reduce this burden on individuals and their families."
More information: Yingtong Li et al, Early Access to First-Seizure Clinics, Subsequent Outcomes, and Factors Associated With Attendance, JAMA Neurology (2024). DOI: 10.1001/jamaneurol.2024.1187