This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
peer-reviewed publication
trusted source
proofread
Study finds gaps in access to proton beam therapy for cancer patients
A new University of Kentucky Markey Cancer Center study reveals that many people with cancer in the U.S. do not have equal access to facilities that offer an advanced form of radiation treatment.
The research, published in JAMA Network Open, is a collaboration between UK Markey Cancer Center, Brown University, MD Anderson Cancer Center and Sidney Kimmel Cancer Center.
The study examined how far people must travel to get to the nearest facility offering proton beam therapy, a type of radiation therapy that uses streams of protons to kill tumor cells. Used to treat cancers of the head and neck and organs such as the brain, eye, lung, spine and prostate, proton therapy can reduce the amount of radiation damage to healthy tissue near a tumor.
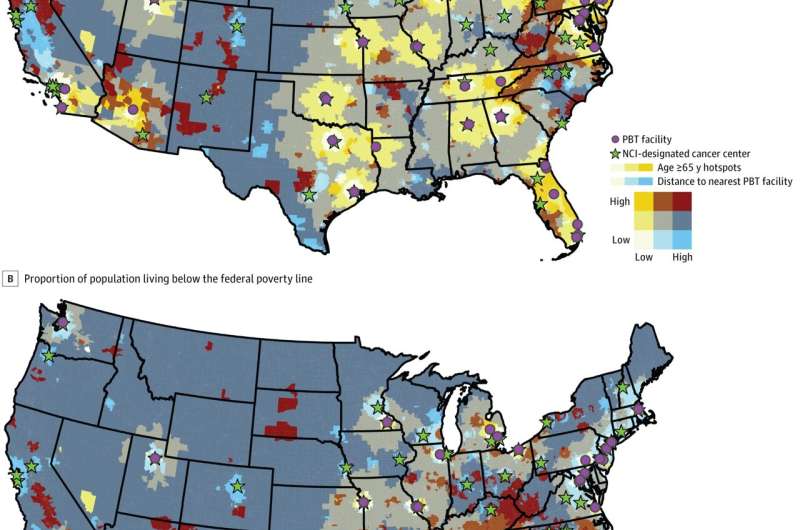
Because the facilities are expensive to build and run, there are a limited number of proton therapy centers in the U.S. The study found that disparities in access existed among certain populations.
"The results suggest these disparities present a barrier to an emerging technology in cancer treatment and inhibit equitable access to ongoing clinical trials," said the study's lead author Todd Burus, a researcher in Markey Cancer Center's Community Impact Office.
The study looked at drive times to proton therapy centers for every area in the country, examining factors like age, income and location. Only about one-third of people in the U.S. live within an hour's drive of a proton therapy center, while more than 16% have to drive four hours or more. Older adults, people with low incomes and those living in rural areas face the biggest hurdles in getting to these centers.
These long travel distances can create significant challenges for patients seeking treatment. Although patients could stay overnight near proton beam therapy centers, most prefer to get care close to home. In addition, insurance often doesn't cover lodging, adding to the cost of cancer treatment.
"These results have broad and important ramifications for patients, radiation oncology clinicians, researchers, cancer center administrators and policy makers," the study concludes. "Being aware of drive-time requirements may also improve shared decision making for clinicians and patients when considering proton beam therapy as a potential treatment option."
More information: Todd Burus et al, Travel-Time Disparities in Access to Proton Beam Therapy for Cancer Treatment, JAMA Network Open (2024). DOI: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2024.10670