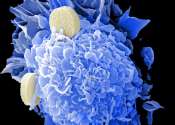
The molecules behind metastasis
Many cancer cells never leave their original tumors. Some cancer cells evolve the ability to migrate to other tissues, but once there cannot manage to form new tumors, and so remain dormant. The deadliest cancer cells are ...
Jan 5, 2023
0
71