An immune system is a collection of biological processes within an organism that protects against disease by identifying and killing pathogens and tumour cells. It detects a wide variety of agents, from viruses to parasitic worms, and needs to distinguish them from the organism's own healthy cells and tissues in order to function properly. Detection is complicated as pathogens can evolve rapidly, producing adaptations that avoid the immune system and allow the pathogens to successfully infect their hosts.
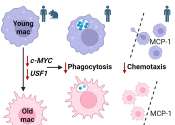
To survive this challenge, multiple mechanisms evolved that recognize and neutralize pathogens. Even simple unicellular organisms such as bacteria possess enzyme systems that protect against viral infections. Other basic immune mechanisms evolved in ancient eukaryotes and remain in their modern descendants, such as plants, fish, reptiles, and insects. These mechanisms include antimicrobial peptides called defensins, phagocytosis, and the complement system. Vertebrates such as humans have even more sophisticated defense mechanisms. The immune systems of vertebrates consist of many types of proteins, cells, organs, and tissues, which interact in an elaborate and dynamic network. As part of this more complex immune response, the human immune system adapts over time to recognise specific pathogens more efficiently. This adaptation process is referred to as "adaptive immunity" or "acquired immunity" and creates immunological memory. Immunological memory created from a primary response to a specific pathogen, provides an enhanced response to secondary encounters with that same, specific pathogen. This process of acquired immunity is the basis of vaccination.
Disorders in the immune system can result in disease. Immunodeficiency occurs when the immune system is less active than normal, resulting in recurring and life-threatening infections. Immunodeficiency can either be the result of a genetic disease, such as severe combined immunodeficiency, or be produced by pharmaceuticals or an infection, such as the acquired immune deficiency syndrome (AIDS) that is caused by the retrovirus HIV. In contrast, autoimmune diseases result from a hyperactive immune system attacking normal tissues as if they were foreign organisms. Common autoimmune diseases include Hashimoto's Thyroiditis, rheumatoid arthritis, diabetes mellitus type 1 and lupus erythematosus. Immunology covers the study of all aspects of the immune system which has significant relevance to human health and diseases. Further investigation in this field is expected to play a serious role in promotion of health and treatment of diseases.