Binge eating linked to comorbidities in obese adults

(HealthDay)—For obese adults, binge eating disorder (BED) may be associated with specific medical comorbidities, according to a study published online March 16 in the International Journal of Eating Disorders.
James E. Mitchell, M.D., from the Neuropsychiatric Research Institute in Fargo, N.D., and colleagues examined whether BED status was associated with medical comorbidities in a cohort of adults scheduled for bariatric surgery. Data were included for 350 participants classified as having BED and 1,875 classified as not having BED.
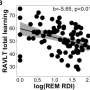
The researchers found that BED status was independently associated with four of 15 comorbidities after adjustment for age, sex, education, and body mass index. BED status was associated with increased odds of impaired glucose levels, (odds ratio [OR], 1.45), high triglycerides (OR, 1.28), and urinary incontinence (OR, 1.3), and with lower odds of severe walking limitations (OR, 0.53). BED status was independently associated with three comorbidities after further adjustment for psychiatric/emotional health indicators: impaired glucose levels (OR, 1.36), cardiovascular disease (OR, 0.5), and severe walking limitations (OR, 0.38). For all variables, Holm's-adjusted P values were greater than 0.05.
"The results suggest the possibility of a contribution of BED to risk of specific medical comorbidities in severely obese adults," the authors write.
More information:
Abstract
Full Text (subscription or payment may be required)
Copyright © 2015 HealthDay. All rights reserved.