Surgery improves quality of life for patients with chronic sinus infection, sleep dysfunction
Patients with chronic rhinosinusitis (sinus infection) and obstructive sleep apnea report a poor quality of life, which is substantially improved following endoscopic sinus surgery, according to a study published online by JAMA Otolaryngology-Head & Neck Surgery.
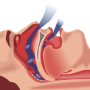
A growing body of literature has highlighted the important links between quality of life (QOL), sleep, and chronic rhinosinusitis (CRS), such that disease severity has been correlated with worse QOL and patients with worse QOL have poor sleep. It is possible that CRS propagates sleep dysfunction through many cofactors including nightly wakening, nasal obstruction, depression and pain, according to background information in the article.
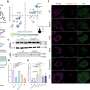
Timothy L. Smith, M.D., M.P.H., of Oregon Health & Science University, Portland, and colleagues investigated the impact of comorbid obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) on CRS disease-specific QOL and sleep dysfunction in patients with CRS following functional endoscopic sinus surgery (FESS). The study included 405 patients with a diagnosis of CRS who underwent FESS. Of these participants, 60 (15 percent) had comorbid OSA. A [total of 285 (70 percent) participants provided preoperative and postoperative survey responses for various measures, with an average of 13.7 months of follow-up.
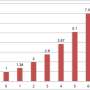
There was no difference found between those with and without OSA in regards to disease severity or CRS disease-specific QOL, poor sleep, or average sleep quality scores prior to surgery. Following FESS, substantial gains in QOL and disease severity were observed for patients with CRS with and without OSA, and these gains were statistically significant. Participants without OSA reported greater improvements on sleep quality.
"Patients with OSA should be treated concurrently for both CRS and OSA to optimize sleep dysfunction and QOL improvement. Future investigations are needed to further elucidate the discordance and underlying mechanisms of sleep improvement between those patients with and without OSA with objective sleep measures," the authors write.
More information: JAMA Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. Published online September 10, 2015. DOI: 10.1001/.jamaoto.2015.1673