Noninvasive ventilation during exercise training beneficial in patients with COPD
Researchers from Turkey's Ege University Department of Biostatistics evaluated the effects of noninvasive ventilation (NIV) and supplemental oxygen during exercise training (ET) and found it to have multiple physiologic benefits in patients with severe COPD. Results showed that supplemental oxygen during exercise helped to reduce hyperinflation and improve respiratory muscle function and exercise capacity.
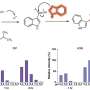
The study consisted of 35 patients with COPD who underwent training for 8 weeks. Each group was randomized to either ET+NIV+O2, ET+O2, or ET alone. While no significant changes were found in ET alone, improvement in depression and walking distance increased in both of the other groups. Results from this study found a decrease in total lung capacity in patients who received ET+NIV+O2 but no significant change in ET+O2 patients.
"The study concluded that adding noninvasive ventilation to oxygen during exercise training in patients with severe COPD was a useful adjunct for improving breathlessness. It reduced hyperinflation and rates of depression, while improving respiratory muscle strength and quality of life measures," said Mark J. Rosen, MD, Master FCCP, CHEST Medical Director.
More information: Further results will be shared during CHEST 2015 on Monday, October 26, at 7:30 AM at Palais des Congrès de Montréal, room 513ef.