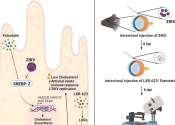
How does SARS-CoV-2 evade our immune defenses?
How does SARS-CoV-2 evade our immune defenses? It's a good question, actually. When SARS-CoV-2 defeats host defenses, we need to know how it does so, and conversely, when host defenses prevail, that also needs to be understood. ...