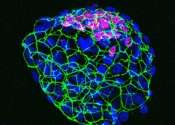
Cellular 'tuning mechanism' builds elegant eyes
How different cells in a multicellular organism acquire their identities remains a fundamental mystery of development. In the eye, for example, the lens contains two cell types—lens epithelial cells and lens fiber cells—the ...
Oct 16, 2018
0
0