Natural products for dementia
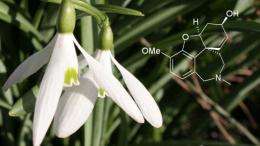
Kew pharmacist, Melanie-Jayne Howes, has been collaborating in research and reviews assessing the role of natural products in the treatment and prevention of dementia.
Dementia is an epidemic of unprecedented proportions, causing a crisis in modern medicine, and with cost estimates exceeding a billion euros in Europe alone. However, effective symptomatic treatments or preventive strategies for dementia, including Alzheimer’s disease (AD), are limited. The few drugs available to alleviate cognitive symptoms include two acetylcholinesterase inhibitors derived from plants. A range of other drugs is often prescribed incidentally to alleviate behavioural and psychological symptoms of dementia, including agitation.
Cinical trail using lemon balm
A recent double-blind, placebo-controlled, randomised trial sponsored by the Alzheimer’s Society, investigated whether Melissa officinalis (lemon balm) oil could treat agitation in AD.
Kew scientists collaborated by performing gas chromatography-mass spectrometry analyses to investigate the authenticity and quality of different M. officinalis oils, and to monitor the chemical stability of the chosen trial formulation throughout the 12-week trial period.
Although there was no evidence that M. officinalis oil was superior to placebo, a positive trend of improved quality of life was reported, but compliance was less than in previous trials (Burns et al., 2011).
Analysis of Withania
Kew scientists have also worked with colleagues from Newcastle University to investigate Withania somnifera root extract for pharmacological activities relevant to dementia. Using liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry, numerous withanolide derivatives were detected in this extract which were neuroprotective against hydrogen peroxide- and β-amyloid-induced toxicity in vitro (Kumar et al., 2010).
Reviews on natural products for dementia
The potential for natural products to provide drug leads for AD has recently been reviewed by Melanie-Jayne Howes (Kew) and colleagues at the Univeristy of Hawaii. The review covers a diverse array of compounds, organised according to their mechanism of action, with the focus primarily on the major hypotheses for drug targets. More than 180 compounds, including those currently in clinical use for symptomatic treatment in AD (e.g. galantamine, originally from Galanthus sp.) are discussed, in addition to the status of natural products in drug development programs (Williams et al., 2011).
Melanie-Jayne Howes and Elaine Perry (Newcastle University) have also reviewed the role of natural products in the treatment and prevention of dementia, with an emphasis on clinical trial evidence, and from the perspective of available epidemiological data (Howes and Perry, 2011; Perry and Howes, 2011).
The investigation of plants with traditional uses that might alleviate symptoms in AD has also been recently reviewed by Kew scientists. The authors discussed those plants with relevant mechanistic and clinical effects that could be pursued as treatment strategies for AD (Howes and Houghton, 2011).
More information:
Article references:
Burns, A., Perry, E., Holmes, C., Francis, P., Morris, J., Howes, M-J.R., Chazot, P., Lees, G. & Ballard, C. (2011) A double-blind placebo-controlled randomised trial of Melissa officinalis oil and donepezil for the treatment of agitation in Alzheimer’s disease. Dement. Geriatr. Cogn. Disord. 31: 158-164.
Howes, M-J.R. & Houghton, P.J. (2011). Ethnobotanical treatment strategies against Alzheimer’s disease. Curr. Alzheimer Res. In press.
Howes, M-J.R. & Perry, E. (2011). The role of phytochemicals in the treatment and prevention of dementia. Drugs & Aging. 28: 439-468.
Kumar, S., Seal, C.J., Howes, M-J.R., Kite, G.C. & Okello, E.J. (2010). In vitro protective effects of Withania somnifera (L.) Dunal root extract against hydrogen peroxide and β-amyloid(1-42)-induced cytotoxicity in differentiated PC12 cells. Phytother. Res. 24: 1567-1574.
Perry, E.K. & Howes, M.-J.R. (2011). Medicinal plants and dementia therapy: Herbal hopes for brain ageing? CNS Neurosci. Ther. DOI: 10.1111/j.1755-5949.2010.00202.x.
Williams, P., Sorribas, A. & Howes, M.-J.R. (2011). Natural products as a source of Alzheimer’s drug leads. Nat. Prod. Rep. 28: 48-77.














