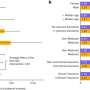
Majority of people unable to pay their medical bills skip medical care

Difficulty paying medical bills is an important predictor of the likelihood that a person will forego medical and prescription drug care and can add to the impact of lack of health insurance and other factors such as income, education level, and health status, according to an article in Population Health Management, a peer-reviewed journal from Mary Ann Liebert, Inc., publishers.
In "Associations Between Difficulty Paying Medical Bills and Forgone Medical and Prescription Drug Care," Kristin Baughman, PhD and coauthors, Northeast Ohio Medical University (Rootstown), Kent State University (Kent, OH), Case Western Reserve University School of Medicine (Cleveland, OH), and Duke University School of Medicine (Durham, NC), examine several variables that could be made worse by unaffordable medical expenses, leading a person not to seek needed medical attention. These relationships can become cyclical, as foregone medical care can negatively impact a person's health, which could affect their employment status and financial resources.
"Once again we have solid research evidence that supports the notion that access to medical care is a vital step toward well being," says Editor-in-Chief David B. Nash, MD, MBA, Dean and Dr. Raymond C. and Doris N. Grandon Professor, Jefferson School of Population Health, Philadelphia, PA.
More information: The article is available free on the Population Health Management website until May 28, 2015.