Periocular basal cell carcinomas can grow rapidly
(HealthDay)—Periocular basal cell carcinomas (pBCCs) have a mean growth rate of 11.2 mm² every 30 days, according to a study published in the April issue of the British Journal of Dermatology.
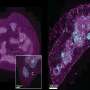
Eugene Tan, M.B.B.S., from the Skin Cancer Institute in Tauranga, New Zealand, and colleagues measured the growth rate and examined the impact of delayed excision on the growth of pBCC. The authors recruited 112 patients with 115 pBCCs who were referred to an oculoplastic service for excision of pBCC. At the first specialist appointment (FSA), the tumor dimensions and patient demographic data were recorded. When the patient attended for tumor excision by Mohs micrographic surgery (MMS), measurement of the pBCC was repeated.
The researchers found that the mean size of the pBCC was 8 × 6 mm, with a mean area of 68.5 mm² at the FSA. There was a 157 ± 87 day average waiting time for MMS. The mean rate of growth was 11.2 mm² every 30 days. There was a mean increase of 41.9 mm² from FSA to MMS. Faster growth rate was seen in association with recurrent tumors, larger tumors at presentation, and male sex.
"Periocular basal cell carcinomas can grow rapidly, and many have aggressive histological subtypes," the authors write. "Rapid growth is more likely in recurrent tumors, larger tumors, and in men."
More information:
Abstract
Full Text (subscription or payment may be required)
Copyright © 2015 HealthDay. All rights reserved.