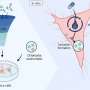
Lasting analgesia for subcompartmental GON block
(HealthDay)—For patients with cervicogenic headache (CH), the classical technique for greater occipital nerve (GON) block results in two weeks of analgesia, compared with at least 24 weeks for the subcompartmental technique, according to a study published in the September issue of Pain Practice.
Gabriela R. Lauretti, M.D., Ph.D., from the University of São Paulo in Brazil, and colleagues compared the efficacy of the GON block using the classical technique with the subcompartmental technique for CH treatment. Thirty patients underwent GON block with 10 mg dexamethasone plus 40 mg lidocaine (5 mL volume). When pain on the visual analog scale was >3 cm, patients were randomized into one of three groups. Each group was submitted to the GON subcompartmental technique under fluoroscopy using 5, 10, or 15 mL final volume.
The researchers found that the classic GON technique correlated with two weeks of analgesia and a reduction in rescue analgesic consumption, compared with 24 weeks after the subcompartmental technique (P < 0.01). Improvement in quality of life was seen at two weeks after the classical technique and at 24 weeks after the suboccipital technique (P < 0.05). The groups were similar regarding analgesia compared with volume of injection (P > 0.05).
"The suboccipital compartmental GON technique resulted in at least 24 compared to two weeks of analgesia when the same dosage of dexamethasone and lidocaine was applied by the classical technique," the authors write.
More information:
Abstract
Full Text (subscription or payment may be required)
Copyright © 2015 HealthDay. All rights reserved.