Successful method reduces myocardial cell damage and extends life of patients
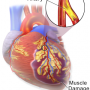
The first sign of a heart attack is chest pain. Treatment in the next six to 10 hours with a method developed by microbiologist Hector Cabrera would reduce damage from three angles: lessening the inflammatory process, vascular activation and cell death in the heart.
The medical procedure was implemented in Mauritius (East Africa) in chronic-degenerative patients with hypertension and diabetes who suffered a heart attack preceded by chest pain. This reduced the cell death rate by 17 percent compared to conventional treatment methods. In 2015, a population study in Malaysia and South Korea began to determine the number of deaths that could be reduced with the application of this new method.
"My first doctoral work was to find bacteria that, by inducing them stress, could naturally produce ribonucleases, which are like scissors that cut the RNA of cells and proliferate in the presence of cancer, and they were targeted to certain types of this ailment, for example, lung cancer. It was my first publication in the scientific community," says Dr. Cabrera, 30 years old.
By studying RNA in cancer, he realized that inflammation and cell death occurred; the next step was to recognize other conditions in which cell damage was involved such as arteriosclerosis or a heart attack with cell death starting from lack of oxygen.
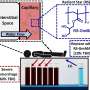
"Together with my team, we saw that in that moment is when RNA is released and we applied different ribonucleases from bacteria and other active human cells. We found that this mechanism can be activated in various organs of the body by applying pressure through a sphygmomanometer; that is, we can induce the release of these active ribonuclease and decrease the magnitude of a heart attack by applying the instrument for five minutes at 200 millimeters of mercury, then letting the body relax and reapplying pressure. Thusm, ribonucleases help reduce the damage by ischemia (lack of oxygen) and its consequences."
Cells are intelligent. When the thrombus forms, there will be a percentage of cells that die immediately and others that will adapt to live without oxygen. During that period of between six to 10 hours after the myocardial happens, the cardiologist releases traditionally applied enzymes into the circulation, thus reopening the artery, and the thrombus is destroyed, but the cells that have adapted die by opening the flow."