Circulating extracellular RNAs linked to insulin resistance

(HealthDay)—Circulating extracellular RNAs (ex-RNAs) are associated with insulin resistance (IR), according to a study published online Feb. 9 in Diabetes Care.
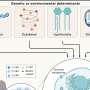
Ravi Shah, M.D., from Massachusetts General Hospital in Boston, and colleagues examined the correlation between ex-RNAs and metabolic phenotypes in 2,317 participants without diabetes in the Framingham Heart Study (FHS) Offspring Cohort. The correlation between candidate ex-RNAs and markers of adiposity was measured. Individuals with diabetes were included in sensitivity analyses. Selected ex-RNAs and metabolites were measured in a separate cohort of 90 overweight/obese youth.
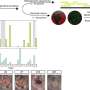
The researchers found that across 391 ex-RNAs in FHS, 18 were associated with IR in age-, sex, and body mass index-adjusted models. Independent of metabolites, miR-122 correlated with IR and regional adiposity in adults and IR in children. Metabolic regulatory roles for miR-122, including regulation of IR pathways, was observed on pathway analysis.
"These results provide translational evidence in support of an important role of ex-RNAs as novel circulating factors implicated in IR," the authors write.
More information: Full Text (subscription or payment may be required)
Copyright © 2017 HealthDay. All rights reserved.