Pediatricians can play a pivotal role in reducing pediatric firearm-related injuries
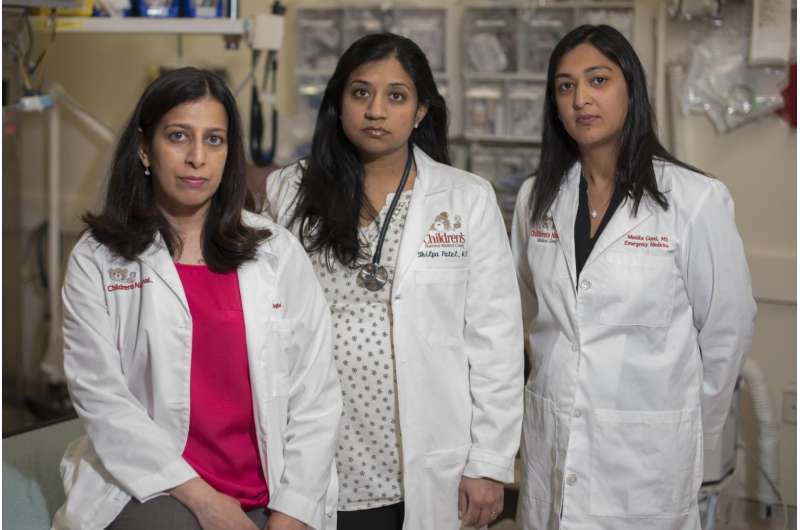
A review led by Children's National Health System researchers published May 23, 2017 in Hospital Pediatrics indicates that while firearms are present in 18 percent to 64 percent of U.S. homes, almost 40 percent of parents erroneously believe that their children are unaware where weapons are stored, and 22 percent of parents wrongly think that their children have never handled household firearms.
For the many children who do encounter firearms in the home, the results can be devastating, the study authors indicate. Firearm-related injuries are the leading cause of injury deaths for youths, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Younger children are more likely to be victims of unintentional firearm injuries, the majority of which occur in the home. Older adolescents are more likely to suffer from intentional injuries. Homicide by firearm is the second-leading cause of death for 15- to 19-year-olds, and suicide by firearm ranks as the third-most common cause of death for children aged 10 to 19. The cost of medical treatment for firearm-related injuries suffered by youths younger than 21 exceeds $330 million, the study indicates.
"While this preventable public health crisis occurs in the home, pediatricians who see children in clinic or at hospitals can play a pivotal role in helping to reduce gun violence," says Kavita Parikh, M.D., M.S.H.S., associate professor of pediatrics in the Division of Hospitalist Medicine at Children's National and study lead author. "In the course of providing care, pediatricians can ask patients and their families about children's access to firearms, can encourage safe storage of firearms in the home and can support research into firearm-related injury prevention."
The review article provides an overview of the prevalence of pediatric firearm-related injuries around the nation and a summary of legislative efforts and health care-related advocacy efforts to reduce firearm injuries around the nation. It includes research by four Children's National co-authors who comprise the institution's newly formed firearm-injury prevention research work group. Alyssa Silver, M.D., Children's Hospital at Montefiore, is another co-author.
The study team found that about 20,000 children are transported to Emergency Departments each year for firearm-related injuries. Youths aged 12 to 19 make up 90 percent of this total. On average, 20 U.S. children and youths are hospitalized daily for firearm-related injuries. About 50 percent of the children who are hospitalized for firearm-related injuries are discharged with a disability.

The researchers identified regional variations in the percentage of households with firearms, as well as differences in firearm ownership by race and ethnicity. Across a number of surveys, 6 percent to nearly 50 percent of families reported storing firearms safely by using such methods as trigger locks and locked storage containers. There is a mismatch in what parents report—with many saying their child would never touch a firearm - compared with children who tell researchers they handle "hidden" firearms, including by pulling the trigger. One survey of 5,000 fifth-graders and their caregivers living in three metropolitan areas found 18 percent had household firearms. Of this group, African American and Latino households had lower odds of firearm ownership than families of white, non-Latino children. Among these survey respondents, families of white non-Latino children were less likely than families of African American children to use safer strategies for firearm storage.
"While public health interventions have had varying degrees of success in improving firearm safety, the most effective programs have offered families free gun safety devices," says Monika Goyal M.D., M.S.C.E., assistant professor of pediatrics and emergency medicine at Children's National and senior study author. "The stark differences in how parents perceive their children would act and the children's own recollections to researchers underscore the importance of the combination of counseling parents to talk to their children about firearms and instituting safe storage practices for household guns."
Sabah F. Iqbal, M.D., assistant professor of pediatrics and emergency medicine at Children's National and study c0-author, adds: "Most families are willing to discuss firearm safety with health care providers. It is encouraging that when families receive safety counseling from health care professionals, they store firearms more safely within the home. Pediatricians need to ask children and their families about the presence of firearms in the home. These essential conversations can occur in any medical setting and need to begin before a child begins to walk and explore their own home."
Screening for access to firearms within the health care setting where youths receive routine care may represent a beneficial strategy, the authors write. A recent survey conducted among 300 adolescents seen in an Emergency Department found that 16 percent reported having a gun in the home and 28 percent said they could access a loaded gun within three hours. About 50 percent of adolescents screened for firearm access said a friend or relative owned a gun.
The study authors also discuss the benefit of "rigorous, well-conducted" research of firearm-related injuries to guide the work of public health agencies, policymakers and pediatricians, as well as supporting state-level laws shown to be effective in preventing firearm injuries, such as universal background checks and firearm identification.
"Rigorous investigations, with the use of validated scoring systems, large comprehensive databases and accurate detailed reporting and surveillance of firearm access and related injury are urgently needed," Shilpa J. Patel, M.D., M.P.H., assistant professor of pediatrics and emergency medicine at Children's National, and co-authors conclude. "A collective, data-driven approach to public health is crucial to halt the epidemic of pediatric firearm-related injury."
More information: Hospital Pediatrics, DOI: 10.1542/hpeds.2016-0146