Scientists develop novel 'dot' system to improve cancer detection
Researchers at Sanford Burnham Prebys Medical Discovery Institute (SBP) have developed a proof-of-concept nanosystem that dramatically improves the visualization of tumors. Published today in Nature Communications, the platform achieves a five-fold increase over existing tumor-specific optical imaging methods. The novel approach generates bright tumor signals by delivering "quantum dots" to cancer cells without any toxic effects.
Xiangyou Liu, Ph.D., and Gary Braun, Ph.D., developed the method in the laboratories of Kazuki Sugahara, M.D., Ph.D., adjunct assistant professor at SBP and adjunct associate research scientist at Columbia University, and Erkki Ruoslahti, M.D., Ph.D., distinguished professor at SBP.
"Tumor imaging is an integral part of cancer detection, treatment and tracking the progress of patients after treatment," says Sugahara. "Although significant progress has been made in the last two decades, better and more sensitive detection, such as the method we are developing, will contribute to more personalized and potentially more effective interventions to improve the clinical outcomes of cancer patients."
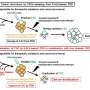
The new method utilizes quantum dots, QDs—tiny particles that emit intense fluorescent signals when exposed to light—and an "etchant" that eliminates background signals. The QDs are delivered intravenously, and some of them leave the bloodstream and cross membranes, entering cancer cells. Fluorescent signals emitted from excess QDs that remain in the bloodstream are then made invisible by injecting the etchant.
"The novelty of our nanosystem is how the etchant works," explains Braun. The etchant and the QDs undergo a "cation exchange" that occurs when zinc in the QDs is swapped for silver in the etchant. Silver-containing QDs lose their fluorescent capabilities, and because the etchant can't cross membranes to reach tumor cells, the QDs that have reached the tumor remain fluorescent. Thus, the entire process eliminates background fluorescence while preserving tumor-specific signals.
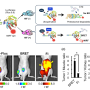
The method was developed using mice harboring human breast, prostate and gastric tumors. QDs were actively delivered to tumors using iRGD, a tumor penetrating peptide that activates a transport pathway that drives the peptide along with bystander molecules—in this case fluorescent QDs—into cancer cells. iRGD methodology was originally developed in Ruoslahti's lab.
To our knowledge, this is the first in vivo example of a background-destroying etchant being used to enhance the specificity of imaging," says Sugahara. "We are encouraged that we were able to achieve a tumor-specific contrast index (CI) between five- and ten-fold greater than the general cut-off for optical imaging, which is 2.5."
"Moving forward we will focus on developing our novel nanosystem to work with routine imaging tests like PET scans and MRIs. In our studies with mice, we use optical imaging, which isn't always practical for humans," Sugahara explains.
A new company is in the process of being founded to further develop the platform for human use.
More information: Xiangyou Liu et al, In vivo cation exchange in quantum dots for tumor-specific imaging, Nature Communications (2017). DOI: 10.1038/s41467-017-00153-y