Livestock-associated MRSAfound among MRSA from humans
The survey results show more frequent detections and geographical dispersion of LA-MRSA in humans in the EU/EEA since 2007, and highlight the public health and veterinary importance of LA-MRSA as a 'One Health' issue. The ECDC advocates for periodic systematic surveys or integrated multi-sectorial surveillance to facilitate control measures.
Livestock-associated meticillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (LA-MRSA) poses a zoonotic risk, particularly for those working in close contact with livestock. Nonetheless, surveillance of LA-MRSA in humans in Europe is currently not systematic, but mainly event-based.
In 2014, the European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control (ECDC) initiated a questionnaire survey to collect data on the numbers of LA-MRSA from human samples at national or regional reference laboratories in EU/EEA countries in 2013. ECDC received responses from 28 reference laboratories from 27 (90%) EU/EEA countries.
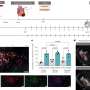
Overall, respondents reported receiving MRSA isolates from 14,291 patients in 2013, of which 13,756 (96%) were typed. LA-MRSA was identified by 17 (89%) of 19 countries with MRSA typing data. Overall, the percentage of typed MRSA isolates that were LA-MRSA was 3.9% (535/13,756). Seven countries reported that MRSA typing was not performed, in 2013, in the responding reference laboratory.
This survey documents the increasing detection and geographical dispersion of LA-MRSA in humans in the EU/EEA since 2007. Moreover, 2014 and 2015 reports from the Nordic countries, Germany, the Netherlands and the UK have subsequently indicated an upward trend in the spread of LA-MRSA across Europe. The absence, in 2013, of MRSA typing in national/regional laboratories in seven countries is therefore of concern.
The results and overall high response rate for this survey highlight both the actual and perceived public health importance of LA-MRSA as a 'One Health' issue in EU/EEA countries. ECDC therefore recommends that EU/EEA countries consider repeating this survey periodically to monitor for changes and systematically map potential reservoirs and transmission pathways. Linkage of multi-sectorial, 'One Health' MRSA data is also encouraged, in order to enable appropriate targeting and monitoring of the effectiveness of control measures.