UN: About 11 percent of drugs in poor countries are fake
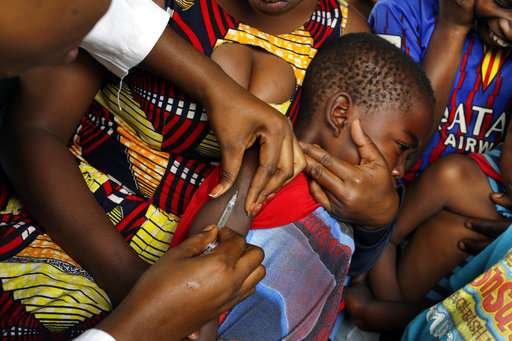
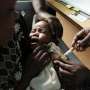
About 11 percent of medicines in developing countries are counterfeit and likely responsible for the deaths of tens of thousands of children from diseases like malaria and pneumonia every year, the World Health Organization said Tuesday.
It's the first attempt by the U.N. health agency to assess the problem. Experts reviewed 100 studies involving more than 48,000 medicines. Drugs for treating malaria and bacterial infections accounted for nearly 65 percent of fake medicines.
WHO's director-general said the problem mostly affects poor countries. Between 72,000 and 169,000 children may be dying from pneumonia every year after receiving bad drugs. Counterfeit medications might be responsible for an additional 116,000 deaths from malaria mostly in sub-Saharan Africa, according to scientists at the University of Edinburgh and London School of Hygiene and Tropical Medicine commissioned by the WHO.
"Imagine a mother who gives up food or other basic needs to pay for her child's treatment, unaware that the medicines are substandard or falsified, and then that treatment causes her child to die," WHO chief Tedros Adhanom Ghebreyesus said in a statement. "This is unacceptable."
Counterfeit drugs include products that have not been approved by regulators, fail to meet quality standards or deliberately misrepresent an ingredient, according to WHO, which published the two reports.
In 2013, WHO set up a voluntary global monitoring system for substandard and fake drugs and has received reports of about 1,500 problematic medicines including drugs that claim to treat heart problems, diabetes, fertility problems, mental health issues and cancer. WHO also reported problems of fake vaccines for diseases including yellow fever and meningitis.
WHO credited the database with saving the lives of several dozen children in Paraguay after an analysis showed they were affected by a contaminated drug contained in a cough medicine that had killed 60 adults in Pakistan several months earlier in 2013.
WHO said the cases of fake medicines it found are only "a small fraction" and that problems may be going unreported. The agency estimated countries are spending about $30 billion on counterfeit drugs.
© 2017 The Associated Press. All rights reserved.