Study estimates misuse of prescribed opioids in the United States

A new Pharmacoepidemiology & Drug Safety study estimates the prevalence and risk factors for self-reported misuse of prescribed opioids in the general adult population.
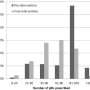
Based on data from the National Survey on Drug Use and Health, the study's investigators estimate that of more than 89 million US adults who used prescription opioids every year, close to 3.9 million (4.4 percent) reported misusing the prescribed medications. Prescribed opioid misuse was most strongly associated with co-occurring misuse of opioids without a prescription, misuse of benzodiazepines, other drug use disorders, history of illegal activity, and psychological distress.
"While most people who are prescribed opioid medications use them as prescribed, a minority tend to use a higher dose, use the medication more frequently, or for a longer time than prescribed," said lead author Dr. Ramin Mojtabai, of Johns Hopkins University. "Prescribers should be especially vigilant about the possibility of misuse among patients who are prescribed more potent opioid medications and prescribed these medications for long-term use."
More information: Ramin Mojtabai et al, Misuse of prescribed opioids in the U nited S tates, Pharmacoepidemiology and Drug Safety (2019). DOI: 10.1002/pds.4743