How the brain perceives time

What happens in the brain when listening to the rhythmic pace of a song, or when waiting for a traffic light to turn green? For the first time, an imaging study shows that a time map exists in a specific area of the human brain, the so-called supplementary motor area (SMA).
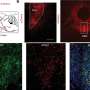
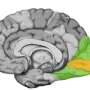
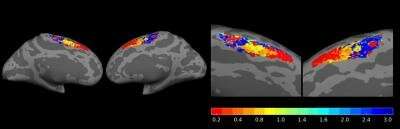
The study, conducted by the team led by SISSA Professor Domenica Bueti and published in PLOS Biology, shows that distinct portions of the SMA, a region of the cerebral cortex important for motor preparation and time perception, respond preferentially to different durations. The portions of the SMA responding to similar durations are in close spatial proximity on the cortical surface, according to an anterior-to-posterior spatial gradient.
The most anterior portions of SMA are greatly active for the shortest duration (200 ms), while the most posterior bits are active for the longest duration (3 sec), the intermediate durations led to the activation of the cortex between those extremes. These novel findings, which are the result of a collaborative effort between SISSA and research institutions in Japan, Switzerland and the Netherlands, are important to gain insights on the computational architecture underlying time perception and they also open up new perspectives to the study of temporal cognition.
The representation of time
"Topography i.e., the fact that neurons processing similar stimulus properties occupy neighbouring positions on the nervous system, is an encoding mechanism widely used in the brain to represent sensory and motor information. For example, there is a body map in our primary somatosensory cortex. In this map, the portions of the cortex receiving tactile information from the hand and the wrist are neighbours compared to those receiving information from the toe," says Domenica Bueti. "Our findings show that a topographic representation exists also for something immaterial like time." Previous studies conducted in humans and other animals have shown the involvement of SMA in time perception. However, none of those previous works clarified how temporal information is represented in this area.
"With our work, we show that in SMA time is represented via topography and duration tuning. The first, as we said earlier, refers to the fact that the portions of SMA responding to similar durations are in close spatial proximity on the cortical surface." The second is duration tuning: "Our results show that different portions of SMA respond preferentially to certain durations in a way that the response is greater for the preferred duration, and become progressively weaker for durations far from the preferred one. Moreover, we show that temporal maps are linked to perception: i.e., the better the map in SMA, the more accurate and precise is duration perception. This is how SMA represents time."
A cutting-edge study
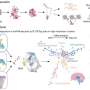
The research was conducted with functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) at ultra-high field i.e., 7 Tesla, available at the Ecole Polytechnique Federale of Lausanne. During the study, two groups of healthy volunteers carried out a temporal discrimination task of visual stimuli i.e., two images displayed in sequence on a computer screen for durations ranging from 200 milliseconds up to 3 seconds. Each volunteer had to decide which of the two images was presented for longer time. While the volunteers carried out the task, their cerebral activity was recorded through fMRI.
"It was an extremely complex study, which took a long time to carry out, and besides SISSA, it involved researchers from Osaka University, Sussex University, the Ecole Polytechnique Federale of Lausanne, the Royal Academy for Arts and Sciences of Amsterdam, Lausanne University and Araya Inc. of Tokyo," explains Domenica Bueti.
Perceiving time: innate or acquired phenomenon?
Many interesting questions arise from these findings. Domenica Bueti says, "We have now to understand whether this time map represents the physical or the perceived time. Does the map change as the perceived duration changes? Does the map change if an observer perceives a stimulus that was physically displayed on the screen for one second, as either longer (for example a second and a half) or shorter (for example, 800 milliseconds)? And are there maps at birth? Or are they the by-product of experience and education? These are important and fascinating questions we would like to investigate with our future research."
More information: Foteini Protopapa et al, Chronotopic maps in human supplementary motor area, PLOS Biology (2019). DOI: 10.1371/journal.pbio.3000026