SCAI releases multi-society endorsed consensus on the classification stages of cardiogenic shock
A newly released expert consensus statement proposes a classification schema for cardiogenic shock (CS) that will facilitate communication in both the clinical and research settings. The document was published online in SCAI's Catheterization and Cardiovascular Interventions journal, and is endorsed by the American College of Cardiology, American Heart Association, the Society of Critical Care Medicine and the Society of Thoracic Surgeons.
Cardiogenic shock is a condition in which the heart, often abruptly, cannot pump enough blood to meet the body's needs (Mayo Clinic). Most often accompanying larger heart attacks such as myocardial infarction (MI), outcomes for patients with cardiogenic shock complicating MI have not significantly improved over the last 30 years despite the development of various percutaneous mechanical circulatory support technologies and the national standard of emergent angioplasty and stenting.
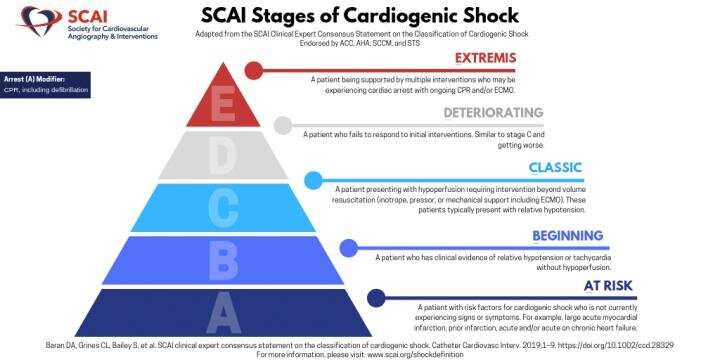
SCAI convened a multi-disciplinary writing group comprised of leading experts in interventional and advanced heart failure, non-invasive cardiology, emergency medicine, critical care, and cardiac nursing to represent the team-based care of these patients. The writing group developed a new five-stage system that is defined by narrative patient descriptions, physical findings, and biochemical/hemodynamic markers, creating a new language that will facilitate rapid assessment, reassessment over time, and communication between providers including hospital systems.
The new CS definition is intended to provide clinicians and researchers with a unified and standardized vocabulary that will translate across all settings. Additionally, the definition aims to facilitate recognition of risk for adverse outcomes and the potential benefit from various interventions and prognosis, with the goal of reducing mortality on both an individual and national scale.
"The main areas we may have failed in the fight to improve mortality in cardiogenic shock is, quite simply, not speaking the same language when describing these patients," said Srihari S. Naidu, MD, FSCAI, former SCAI Trustee and chair of the writing group. "Without that, we can't even begin to understand these patients, how sick they are, what might work and what does not work. This is the most important first step, and it is important to use this classification system to reset our understanding of cardiogenic shock and restart the trials very much needed in this space."
More information: David A. Baran et al, SCAI clinical expert consensus statement on the classification of cardiogenic shock, Catheterization and Cardiovascular Interventions (2019). DOI: 10.1002/ccd.28329