Intestinal immune cell interactions
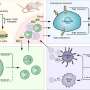
Multiple types of immune cells are interspersed among the epithelial cells lining the intestines and are considered to be a first line of defense against pathogens. The survival and interaction of these intraepithelial lymphocytes and their roles in intestinal inflammation are not well understood.
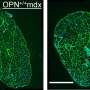
Ali Nazmi, Ph.D., Danyvid Olivares-Villagómez, Ph.D., and colleagues have examined the effect of one type of intraepithelial lymphocyte (iCD8alpha) on another (ILC1-like). Using mice with reduced numbers of iCD8alpha cells, they found that these cells play a critical role in the survival of ILC1-like cells, and that this effect is partly mediated by the factor osteopontin.
In a mouse model of intestinal inflammation that involves ILC1-like cells, reduced iCD8alpha cell numbers resulted in milder inflammation and treatment with osteopontin increased disease severity.
The findings, reported in PLOS ONE, implicate iCD8alpha cells in ILC1-like cell survival and intestinal inflammation and add to the growing roles of osteopontin in various biological processes.
More information: Ali Nazmi et al. Innate CD8αα+ cells promote ILC1-like intraepithelial lymphocyte homeostasis and intestinal inflammation, PLOS ONE (2019). DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0215883