How a South Indian script is changing the way science views parasite
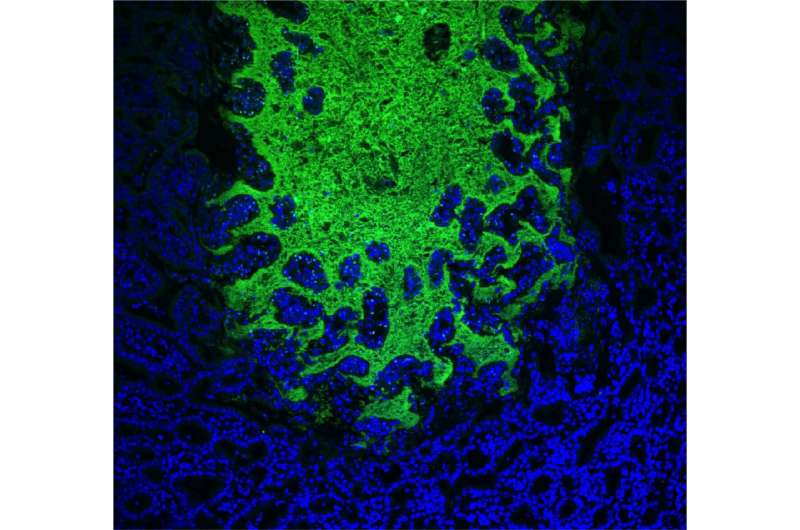
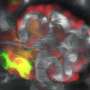
Toxoplasma gondii is an insidious little parasite that infects one out of three people on the planet. A unique partnership between an engineer and a scientist produced data that challenged prevailing wisdom about this parasite's behavior and revealed potential targets for treatment.
T. gondii infects humans two different ways, but one particular avenue—exposure to feces from infected cats—makes it colloquially known as "kitty litter disease." The other form, typically acquired by consuming raw or undercooked meat, develop as tissue cysts in the muscles and brain of its host where, according to prevailing scientific wisdom, it remains in a dormant state capable of reactivation, though the mechanisms by which it reactivates are unknown.
According to Anthony Sinai Ph.D. of the University of Kentucky's College of Medicine, the real trouble begins when these parasites reactivate in the brain, to cause potentially fatal toxoplasmic encephalitis. Tennis legend Arthur Ashe is perhaps the most well-known person to succumb to the disease.
"Reactivation in the context of immune suppression caused by active HIV-AIDS, chemotherapy or organ transplant makes these tissue cysts ticking time bombs in the brain," Sinai said.
For about 40 years, the accepted scientific notion was that the parasites residing in these cysts were dormant. The primary treatment objective, said Sinai, was to reduce the number of cysts or to prevent them from reactivating. The problem was that existing treatments weren't at all effective, and methods to screen for new drugs was inefficient and unproductive.
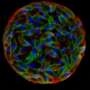
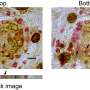
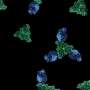
"Previously, we had simply counted the number of cysts, overlooking the fact that each cyst had a wildly different number of parasites contained within," he said. Sinai wanted to know how many parasites were contained in each cyst, but quantifying that data for dozens of cysts would require a manual count, which he estimated would take a "skilled, motivated technician" about a week to accomplish, with notable potential for human error.
Then, at a campus meeting, Sinai met Abhijit Patwardhan, Ph.D., of the UK's College of Engineering, and told him his dilemma. Patwardhan developed software for Sinai that could quantify the number of parasites in a cyst in a fraction of the time—less than an hour, and with complete accuracy.
What's more, said Sinai, the software showed that there was a lot more diversity and heterogeneity within these cysts, suggesting something else was afoot. It led the team to ask what at the time was a "very heretical" question: are these parasites actually dividing when they've previously been considered completely dormant?
"Abhijit started to recognize patterns in the numbers that as a biologist I was glossing over, but as a mathematician and an engineer he was seeing," said Sinai. "This this was something really unique: we were looking at the same data and seeing completely different things that were actually tied into each other."
Like two pieces of the puzzle, Sinai's and Patwardhan's viewpoints merged to uncover patterns inside individual parasites that revealed unprecedented insights into their physiology. This, Sinai said, was key to understanding the basis for drug resistance, identification of novel drug targets and exposing the mechanisms governing reactivation.
Patwardhan said his "light bulb moment" came from an unexpected place: the southern part of India.
"Some structures within the parasites look like squiggles, which reminded me of the Malayalam script used in the southern part of India," he said. "I realized that this challenge was really no different than training a computer to recognize handwritten script."
Patwardhan's work demonstrated that not only were these parasites actively replicating, but they were doing so with a level of complexity that nobody had previously appreciated.
"We effectively turned the field upside down, where now one is really forced to reconsider a lot of what had been taken for granted" about the parasite's life cycle, Sinai said.

The dogma-defying finding—and the technology Patwardhan cleverly adapted to unearth it—is being leveraged into a computational modeling framework to gain predictive insights into infection progression, with significant potential to improve treatment strategies.
"Immunosuppressed patients who are infected with the parasite must be on prophylactic drugs in case the parasite reactivates. However, the drugs have significant side effects, which stifles treatment compliance," Sinai said.
"If we're able to predict when a patient is at risk, maybe we can adjust treatment—even let patients go on a drug holiday—when the chance of the parasites reactivating is really low."
Sinai credits Patwardhan's slightly different vantage point as the catalyst for this important new discovery.
"[Patwardhan] saw patterns that nobody had even predicted existed five years ago, do in fact exist, and may be exploited," said Sinai. "To now be a few steps away from being able to apply it potentially in clinical practice, in testing new drugs, in driving how drug treatment happens, that's truly amazing."
Patwardhan said that Sinai's willingness to challenge the prevailing wisdom in his field was critical.
"Not many investigators are willing to do so; there is professional risk that comes with it," Patwardhan said.
The team's work has caught the eye of the NIH, which has awarded the pair a $1.1 million, three-year grant to continue their study.