Potential therapeutic effects of dipyridamole in the severely ill patients with COVID-19
Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) infection can cause acute respiratory distress syndrome, hypercoagulability, hypertension, and multiorgan dysfunction. In recent months, SARS-CoV-2 has gradually spread to more than 200 countries and regions, resulting in more than 500,000 deaths globally.
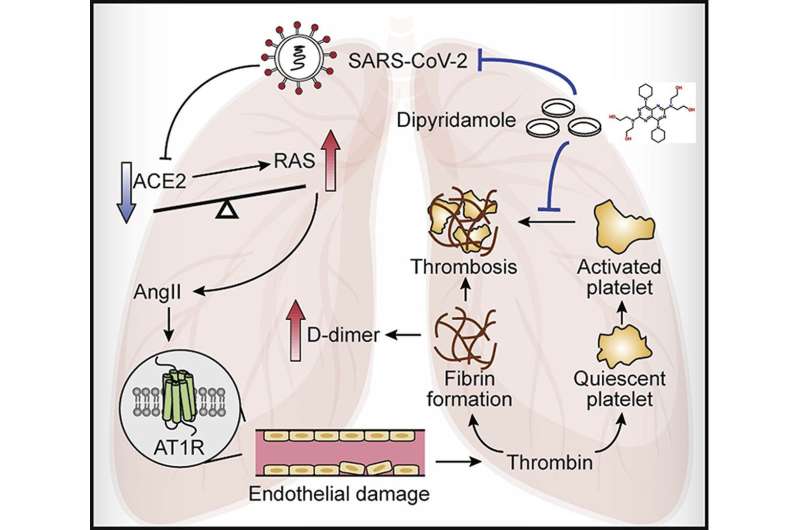
Effective antivirals with safe clinical profile are urgently needed to improve the overall prognosis. In an analysis of a randomly collected cohort of 124 patients with COVID-19, the authors found that hypercoagulability as indicated by elevated concentrations of D-dimers was associated with disease severity. By virtual screening of a U.S. FDA approved drug library, the authors identified an anticoagulation agent dipyridamole (DIP) in silico, which suppressed SARS-CoV-2 replication invitro.
In a proof-of-concept trial involving 31 patients with COVID-19, DIP supplementation was associated with significantly decreased concentrations of D-dimers (P<0.05), increased lymphocyte and platelet recovery in the circulation, and markedly improved clinical outcomes for the severely ill patients in comparison to the control patients. In summary, DIP could be used for the treatment of severely ill patients with COVID-19 through antiviral and anticoagulation effects.
More information: Xiaoyan Liu et al. Potential therapeutic effects of dipyridamole in the severely ill patients with COVID-19, Acta Pharmaceutica Sinica B (2020). DOI: 10.1016/j.apsb.2020.04.008