Physicians bring attention to overlooked issue of malnutrition among those with obesity
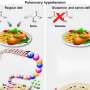
A new editorial accompanying a study published in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology is bringing attention to the underappreciated and often overlooked issue of malnutrition among those who are obese. Malnutrition is defined as faulty nutrition due to inadequate or unbalanced intake of nutrients. It is often incorrectly perceived as an illness that primarily affects those who are underweight, yet a recent study examining acute coronary disease (ACD) found malnourishment is an important underlying factor in the disease. In fact, about half of those found to be malnourished were overweight or obese.
"Malnutrition is a largely under-recognized and undertreated condition in patients with increased body mass index, as increased abdominal girth is too often mistaken for overnutrition rather than undernutrition," said Andrew Freeman, MD, director of cardiovascular prevention and wellness at National Jewish Health and co-author of the editorial. "It's important to dispel the thought that weight is correlated with food quality and that obese patients are not at risk of malnutrition."
The ACD study is just the latest evidence that underscores the prevalence of malnutrition among obese individuals and how it contributes to serious health complications. In fact, the World Health Organization reports that malnutrition affects more than four times more overweight or obese individuals than those who are underweight.
"It is imperative that individuals undergo nutritional assessments and are offered counseling and resources to ensure they are taking in the right nutrients to adequately fuel their body," Dr. Freeman said. "If left untreated, malnutrition leads to serious health conditions including diabetes, hypertension and heart disease."
While it is well-documented in the scientific community that malnutrition causes these health concerns, obese patients who are seen for these conditions often do not undergo nutritional screening, especially in cardiology. Recognizing that overweight patients often have poor diet quality can help shift the conversation in the patient-physician visit toward improving nutritional status.
"Paying lip service with the usual phrases, such as 'Be sure to exercise and eat right,' simply doesn't cut it. It behooves us as a profession to ensure adequate training and competency in the delivery of care in the lifestyle space," Dr. Freeman said. "Clinicians should be well-versed in the dietary patterns known to reduce or even reverse cardiovascular disease, as well as physical activity guidelines and self-care practices such as stress relief, mindfulness and good, quality sleep."
Monitoring each of these lifestyle components can lead to marked improvements in many chronic diseases. This new paper highlights an urgent call to action: it is time for the medical community to arm itself with the most cost effective and powerful tool in the battle against heart disease and other common health conditions: nutrition and lifestyle medicine.
Studies have previously shown that eating whole grains, legumes, fruits, vegetables, nuts, and seeds are beneficial in reducing blood pressure, blood glucose, cholesterol and inflammatory markers. Treatment of at-risk patients must include counseling on how to shift toward a diet that is rich in these healthier food options. In fact, many hospitalizations for life-threatening events can be valuable teaching moments to truly affect care and change treatment trajectories.
More information: Andrew M. Freeman et al, Malnutrition in the Obese, Journal of the American College of Cardiology (2020). DOI: 10.1016/j.jacc.2020.06.059