Research shows the intrinsically nonlinear nature of receptive fields in vision
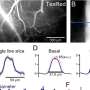
The receptive field (RF) of a neuron is the term applied to the space in which the presence of a stimulus alters the response of the same neuron. The responses of visual neurons, as well as visual perception phenomena in general, are highly nonlinear functions of the visual input (in mathematics, nonlinear systems represent phenomena whose behavior cannot be expressed as the sum of the behaviors of its descriptors).
Conversely, vision models used in science are based on the notion of linear receptive field; in artificial intelligence and machine learning, as artificial neural networks are based on classical models of vision, also use linear receptive fields. "Modeling vision based on a linear receptive field poses several inherent problems: it changes with each input, it presupposes a set of basis functions for the visual system, and it conflicts with recent studies on dendritic computations," asserts Marcelo Bertalmío, first author of a study recently published in the journal Scientific Reports.
The paper proposes modeling the receptive field in a nonlinear manner, introducing the concept of intrinsically nonlinear receptive field or INRF
The paper proposes modeling the receptive field in a nonlinear manner, introducing the intrinsically nonlinear receptive field or INRF. A study conducted by Marcelo Bertalmío, Alex Gómez-Villa, Adrián Martín, Javier Vázquez-Corral and David Kane, researchers with the UPF Department of Information and Communication Technologies (DTIC), together with Jesús Malo, a researcher from the University of Valencia.
An approach with broad implications
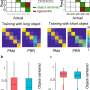
The INRF, apart from being more physiologically plausible and embodying the efficient representation principle, has a key property of wide-ranging implications: for several vision science phenomena where a linear RF must vary with the input in order to predict responses, while an RF linear varies for each stimulus, the INRF can remain constant under different stimuli.
Bertalmío adds, "We have also proved that artificial neural networks with INRF modules instead of linear filters have a remarkably improved performance and better emulate basic human perception." This research highlights the intrinsically nonlinear nature of receptive fields in vision and suggests a paradigm shift for both vision science and for artificial intelligence.
More information: Marcelo Bertalmío et al, Evidence for the intrinsically nonlinear nature of receptive fields in vision, Scientific Reports (2020). DOI: 10.1038/s41598-020-73113-0