Laser therapy promising for drug-resistant child epilepsy

(HealthDay)—More than half of children treated with magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)-guided laser interstitial thermal therapy (MRgLITT) achieve seizure freedom at one-year follow-up, according to a study presented at the annual meeting of the American Epilepsy Society, held virtually from Dec. 4 to 8.
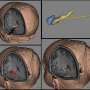
Omar Yossofzai, from the University of Toronto, and colleagues used data from the MRgLITT registry to evaluate outcomes of MRgLITT in 129 children (mean age, 10.7 years) with drug-resistant epilepsy seen at six U.S. and two Canadian pediatric epilepsy surgery centers.
The researchers found that 86 percent of patients had abnormal MRI findings, with hypothalamic hamartoma as the most common lesion (33 cases), followed by focal cortical dysplasia (23 cases). In 22 percent of patients, there were complications relating to MRgLITT, including transient neurologic deficits (16 cases) and permanent neurologic deficits (two cases). One patient died within 30 days after MRgLITT. Mean length of hospital stay was 3.2 days. Seizure freedom was reported in just over half of 93 patients (56 percent) for whom one-year seizure outcome data were available. Twelve patients underwent more than one MRgLITT procedure, and seven of these patients achieved seizure freedom.
"Compared to surgery, MRI-guided laser therapy can help reduce the risk of injury to critical brain structures and minimize serious neurological deficits," a coauthor said in a statement.
More information:
Press Release
More Information
Copyright © 2020 HealthDay. All rights reserved.