Does where older US adults die affect their wellbeing at the end of life?
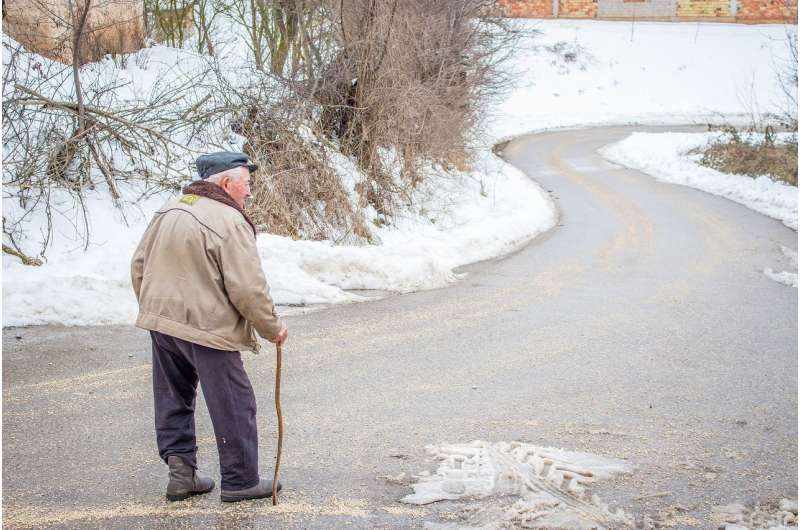

Where people die can affect the quality of their deaths and the end-of-life care that they receive. A study published in the Journal of the American Geriatrics Society found that satisfaction with end-of-life care was rated highest when individuals died at home.
Analyzing data from the National Health and Aging Trends Study of community-dwelling Medicare beneficiaries who died at age 65 years or older, investigators found that the most frequent place of death for persons with cognitive impairment was in the home, but cognitively healthy persons were equally as likely to die at home or in the hospital. Regardless of their cognitive health, individuals who received hospice care were more likely to die at home.
"Our findings suggest that older adults' preference for place of death should be a central component of advance care planning, and the receipt of hospice care may be a key to achieving that preference," said lead author Natalie G. Regier, Ph.D., of the Johns Hopkins University School of Nursing.
More information: Natalie G. Regier et al, Place of Death for Persons With and Without Cognitive Impairment in the United States, Journal of the American Geriatrics Society (2021). DOI: 10.1111/jgs.16979