Droperidol most effective sedation medication for agitation with less sides effects
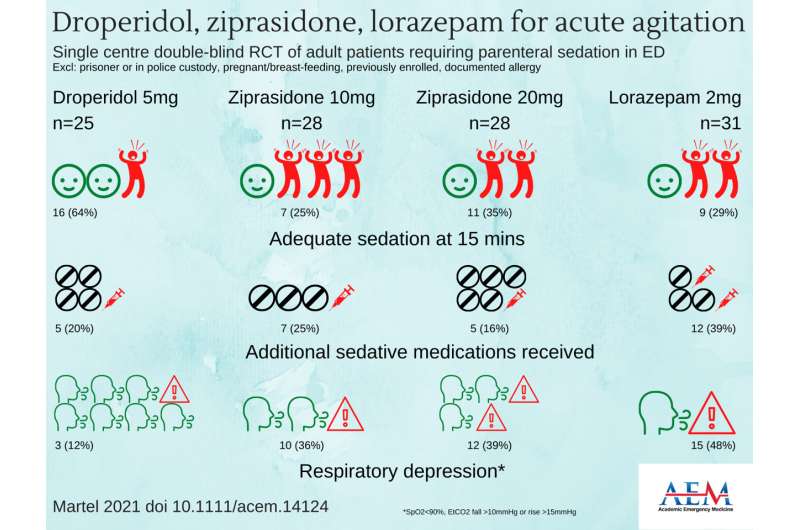
In a randomized, double-blind trial of patients with acute undifferentiated agitation in the emergency department, droperidol was more effective for sedation and was associated with fewer episodes of respiratory depression than lorazepam or either dose of ziprasidone. This is the conclusion of Randomized Double-blind Trial of Intramuscular Droperidol, Ziprasidone, and Lorazepam for Acute Undifferentiated Agitation in the Emergency Department, to be published in the April 2021 issue of Academic Emergency Medicine (AEM), a journal of the Society for Academic Emergency Medicine (SAEM).
Agitation is a common presentation in emergency medicine, ranging from a state of restlessness to overtly violent behavior and can result in injury to both patients and their caregivers. The purpose of this study was to compare intramuscular droperidol, ziprasidone, and lorazepam in patients with acute agitation in the emergency department, using the proportion of patients adequately sedated at 15 minutes as the primary outcome measure. Secondary outcomes included rates of rescue medication, respiratory depression, adverse medication effects, and emergency department length of stay. The authors suggest that larger studies are needed to confirm these findings, particularly to address safety outcomes.
The lead author of the study is Marc L. Martel, of the Department of Emergency Medicine, Hennepin County Medical Center, Minneapolis, Minnesota.
The findings of the study are discussed with Dr. Martel in a recent AEM podcast titled, I Can't Fight This Med Any Longer—Droperidol for Acute Agitation.
More information: Marc L. Martel et al, Randomized Double‐blind Trial of Intramuscular Droperidol, Ziprasidone, and Lorazepam for Acute Undifferentiated Agitation in the Emergency Department, Academic Emergency Medicine (2020). DOI: 10.1111/acem.14124