Research may help identify more dangerous strains of the virus that causes COVID-19
Viral mutations during the COVID-19 pandemic could cause the SARS-CoV-2 virus to become more dangerous. A new study published in Genetic Epidemiology has examined the genetic code of SARS-CoV-2 viruses that have infected patients, looking for links between different mutations and patient deaths.
For the study, investigators analyzed 7,548 SARS-CoV-2 genomes of COVID-19 patients worldwide and looked for an association between genomic variants and mortality. In total, 29,891 locations in the viral genome were assessed.
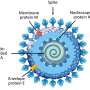
One location was significantly linked with patient mortality. Mutations at this location cause changes in part of the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein, which plays a key role in viral entry into host cells.
"When, in the fall of 2020, we applied methodology from genome-wide association studies to COVID-19 genomes, we noticed one locus in the COVID-19 genomes from Brazil that was associated with mortality and that later became part of the definition of the P.1 strain from Brazil," said co-lead author Georg Hahn, Ph.D., of Harvard University. The P1. strain was behind a deadly COVID-19 surge in the Latin American country. It's more contagious and more resistant to antibodies than the original strain.
More information: Georg Hahn et al, Genome‐wide association analysis of COVID‐19 mortality risk in SARS‐CoV‐2 genomes identifies mutation in the SARS‐CoV‐2 spike protein that colocalizes with P.1 of the Brazilian strain, Genetic Epidemiology (2021). DOI: 10.1002/gepi.22421