'ASCENT' makes it easier to study the electrical stimulation of nerves
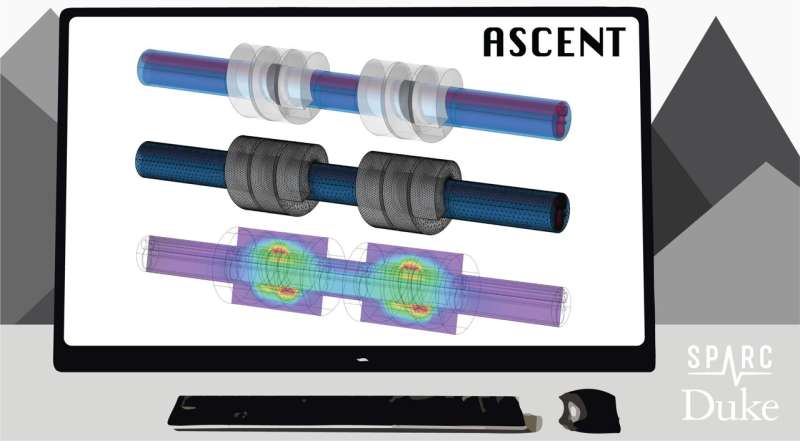

Biomedical engineers at Duke University have developed an open-source software platform that automates 3D electrical nerve stimulation modeling. This may allow researchers to predict how specific nerves will respond to different patterns of stimulation from custom electrodes.
The researchers hope the platform will help researchers create accurate models of new therapies for a variety of diseases, including diabetes, rheumatoid arthritis and cardiovascular disease.
Like a pacemaker for the heart, nerve stimulation devices are implanted in the body and programmed to send targeted pulses of electricity into nerves. These electrical pulses may initiate or suppress signals in the nerve, changing the regulation of organ functions and possibly treating disease. Nerve stimulation is a promising alternative to drugs in some cases..
This research appears online August 26 in the journal PLOS Computational Biology.
Certain electrical stimulation therapies, like vagus nerve stimulation, have already proven to be an effective treatment for illnesses like epilepsy and depression in patients who don't respond to traditional drug therapies.
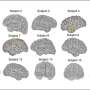
"Despite promising preclinical data, translating nerve stimulation to the clinic is challenging because there is a lot of variability in neural anatomy between animals and humans and even person to person," said Nicole Pelot, a research director in the biomedical engineering lab of Warren Grill at Duke University. "These variabilities require choosing different electrodes or stimulation parameters to achieve a targeted response, which can be a bit of a guessing game."
While computational modeling allows researchers to avoid some of guesswork in electrical stimulation, the modeling process is highly complex, which usually restricts its use to expert developers and limits model reproducibility and reuse. Grill, the Edmund T. Pratt, Jr. School Distinguished Professor of Biomedical Engineering at Duke, has spent the last four years with his colleagues developing a solution.
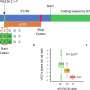
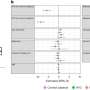
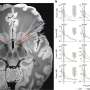
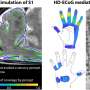
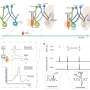
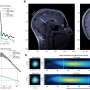
Grill said ASCENT, or Automated Simulations to Characterize Electrical Nerve Thresholds, makes modeling nerve stimulation more accessible, reproducible and efficient. It allows researchers to define a variety of information, like nerve geometry, fiber models, electrode design and stimulation waveforms, and then simulate a nerve's response to the electrical pulses.
ASCENT'S automation allows users to replicate models from previously published research, turning a process that could take years into something that may take just a few weeks or days..
"We designed the code so it's very expandable," added Jake Cariello, an undergraduate research assistant in the Grill lab. "We broke down the complex system into its sub-components, and each of those sub-components is customizable."
ASCENT is an open-source project and is free for users to access, as part of the National Institutes of Health Common Fund's Stimulating Peripheral Activity to Relieve Conditions program (SPARC). The ASCENT software is available for download here.
"A tool that is this specialized is usually inaccessible to more novice users," said Eric Musselman, a Ph.D. student in the Grill lab. "We hope ASCENT will help push the science forward as more researchers are able to design and interpret therapeutic interventions using computational models."
More information: ASCENT (Automated Simulations to Characterize Electrical Nerve Thresholds): A pipeline for sample-specific computational modeling of electrical stimulation of peripheral nerves, PLOS Computational Biology (2021). DOI: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1009285