New therapeutic options for childhood inflammatory bowel disease
Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) affects approximately 40,000 patients in Ireland, with 25% of these cases first arising during childhood. Globally, the prevalence for IBD is 396 cases per 100,000 persons annually. Symptoms include abdominal pain, persistent diarrhea, weight loss and fatigue. The exact cause of the disease remains unknown.
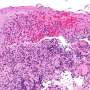
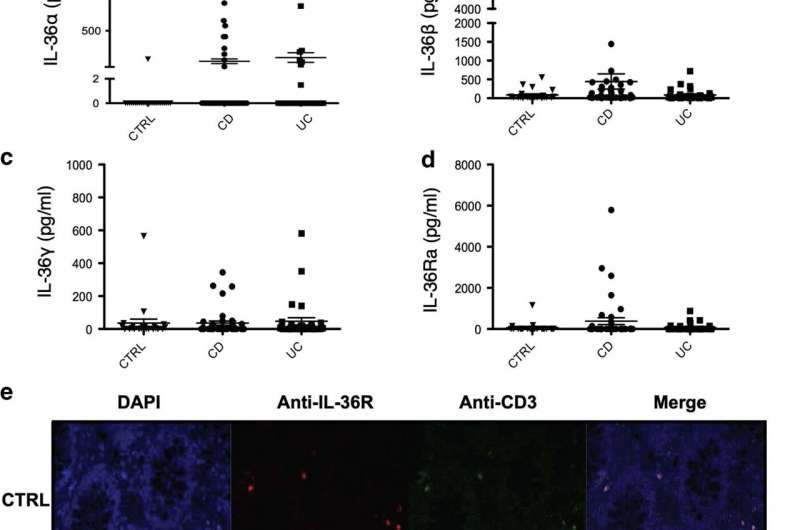
Researchers from Trinity's School of Medicine, working closely with pediatric gastroenterologists at CHI-Crumlin, have previously shown that small proteins known as IL-36 cytokines are 'switched on' in the inflamed intestines of children with newly diagnosed IBD. However, it is still not fully understood how IL-36 cytokines drive disease.
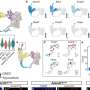
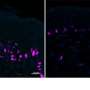
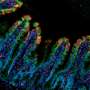
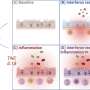
Now, new research from the team addresses this by demonstrating how IL-36 can instruct proinflammatory CD4+ T cells to accumulate in the inflamed intestine and worsen disease. Identifying how these proteins promote disease progression will be invaluable in advancing efforts to target their activity among IBD patients as a new therapeutic option. The study is published in the journal Mucosal Immunology.
IL-36 acts as an instructive signal to drive inflammation in different tissue sites. Its activity is perhaps best characterized in the skin where it is thought to play an important role in driving chronic inflammation in diseases such as psoriasis. Normally the activity of IL-36 is tightly regulated in healthy tissues to ensure that inappropriate activity does not result in chronic inflammation. For ill-defined reasons this regulation appears to be lost in IBD.
The key finding of the study identifies how IL-36 can cause the accumulation of the damaging CD4+ T cell in the inflamed intestine, where they play a central role in driving the inflammation observed in IBD. These findings build upon the team's earlier work which identified that IL-36 cytokines were elevated among children with IBD and was associated with worsening disease outcomes.
Identifying how these proteins promote disease progression offers fresh insights and will advance efforts to target their activity among IBD patients as a new therapeutic option.
This study is part of a long-standing program of translational research between Trinity and pediatric gastroenterologists led by Professor Seamus Hussey at the National Children's Research Centre and CHI Crumlin, which tries to understand the causes of IBD onset during its earliest stages in children/adolescents.
Patrick Walsh, Associate Professor in Pediatric Immunology, Department Of Clinical Medicine at Trinity's School Of Medicine, said:
"These results shed new light on how a potential new therapeutic target can promote the early pathogenesis of IBD. Gaining a deeper understanding of how IBD develops during its earliest stages, in childhood and adolescence, is critically important in efforts to design new and improved treatment options for these patients as they transition to adulthood."
More information: Gemma Leon et al, IL-36 cytokines imprint a colitogenic phenotype on CD4+ T helper cells, Mucosal Immunology (2022). DOI: 10.1038/s41385-022-00488-w