Research team proves how neurotransmitter may be key in controlling Alzheimer's toxicity
With nearly 50 million dementia patients worldwide, Alzheimers's disease is the most common neurodegenerative disease. Its main symptom is the impairment of general cognitive abilities, including the ability to speak or to remember. The importance of finding a cure is widely understood with an increasingly aging population and life expectancy being ever-extended. However, even the cause of the grim disease is yet to be given a clear definition.
A KAIST research team in the Department of Chemistry led by professor Mi Hee Lim took on a lead to discovered a new role for somatostatin, a protein-based neurotransmitter, in reducing the toxicity caused in the pathogenic mechanism taken towards development of Alzheimer's disease. The study was published in the July issue of Nature Chemistry.
According to the amyloid hypothesis, the abnormal deposition of Aβ proteins causes death of neuronal cells. While Aβ agglomerations make up most of the aged plaques through fibrosis, and in recent studies, high concentrations of transitional metal were found in the plaques from Alzheimer's patients.
This suggests a close interaction between metallic ions and Aβ, which accelerates the fibrosis of proteins. Copper in particular is a redox-activating transition metal that can produce large amounts of oxygen and cause serious oxidative stress on cell organelles. Aβ proteins and transition metals can closely interact with neurotransmitters at synapses, but the direct effects of such abnormalities on the structure and function of neurotransmitters are yet to be understood.
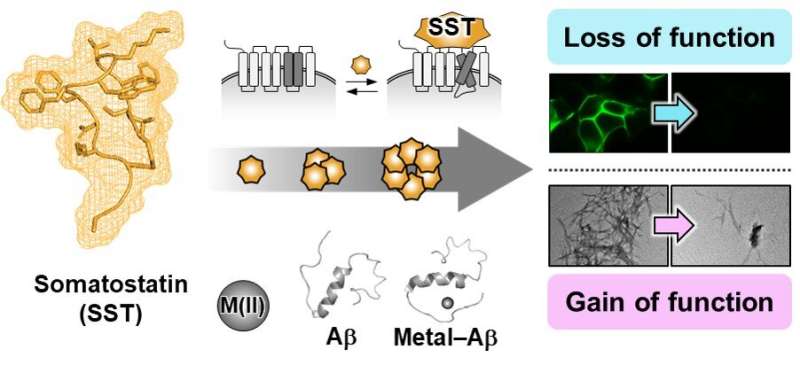
In their research, Professor Lim's team discovered that when somatostatin, the protein-based neurotransmitter, is met with copper, Aβ, and metal-Aβ complexes, self-aggregates and ceases to perform its innate function of transmitting neural signals, but begins to attenuate the toxicity and agglomeration of metal-Aβ complexes.
This research, by Dr. Jiyeon Han et al. from the KAIST Department of Chemistry, revealed the coordination structure between copper and somatostatin at a molecular level through which it suggested the agglomeration mechanism, and discovered the effects of somatostatin on Aβ agglomeration path depending on the presence or absence of metals. The team has further confirmed somatostatin's receptor binding, interactions with cell membranes, and effects on cell toxicity for the first time to receive international attention.
Professor Mi Hee Lim says that "this research has great significance in having discovered a new role of neurotransmitters in the pathogenesis of Alzheimer's disease."
"We expect this research to contribute to defining the pathogenic network of neurodegenerative diseases caused by aging, and to the development of future biomarkers and medicine," she added.
More information: Jiyeon Han et al, Conformational and functional changes of the native neuropeptide somatostatin occur in the presence of copper and amyloid-β, Nature Chemistry (2022). DOI: 10.1038/s41557-022-00984-3