Young hip surgery patients can avoid repeat surgeries with better prediction methods
Young patients undergoing hip surgery who have a shallower hip bone socket are at risk for a repeat operation, according to research presented today at the American Orthopedic Society of Sports Medicine 2022 Annual Meeting.
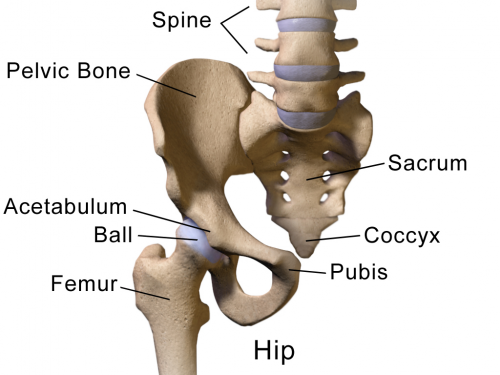
Femoroacetabular impingement is a condition in which extra bone grows along one or both bones that form the hip joint—giving the bones an irregular shape. Because they do not fit together perfectly, the bones rub against each other during movement.
To help orthopedic surgeons better understand radiographic parameters associated with successful primary surgery, Philip A. Serbin, MD, Scottish Rite for Children in Dallas, conducted a prospective study to determine pre-operative radiographic parameters that predict re-operation for FAI, and secondarily, correlate radiographic measures and outcomes in these patients.
Dr. Serbin and colleagues enrolled 87 patients under age 19 (average age 16.27 years with 73.6 percent of patients female) who underwent surgery for FAI.
Enrolled patients underwent primary surgery (56 surgical dislocations vs. 31 arthroscopes) for FAI. Ten of the patients underwent re-operation (11.5%) at an average of 20.6 months from primary surgery. No differences were found in demographics, activity, surgery type, labral disease, or alpha angle for re-operation vs. non-reoperation.
The Lateral Center-Edge Angle (LCEA), the Femoro-Epiphyseal Acetabular Roof (FEAR) Index, and Sharps angle were significantly different (p<0.05).
Dr. Serbin's analysis indicated that patients with scores of LCEA less than 21 and FEAR index greater than -8.8 were at heightened risk of reoperation. Of the patients with LCEA less than 21°, 46% underwent a reoperation compared to those with LCEA greater than 21° (6%). In patients with FEAR index less than -8.8, 32% underwent a reoperation compared to patients greater than -8.8 (5%). Patients who achieved MCID (61.9%) had lower BMI, worse pre-operative PROs, and better post-operative PROs at 2 years. Alpha and Sharp's angles were positively correlated with 2+ year PROs, while LCEA was negatively correlated (p<0.05).
Dr. Serbin reported that in patients undergoing treatment for FAI, a re-operation was associated with radiographic signs of hip dysplasia, indicating that patients with a shallower acetabulum are at risk for a repeat operation.
"Surgeons can utilize these parameters to help in surgical decision making, better predict outcomes, and counsel patients about the need for potential subsequent surgery," Dr. Serbin reported.