Discovery of small molecule Gαq/11 protein inhibitors against uveal melanoma
Constitutively activated G proteins caused by specific mutations mediate the development of multiple malignancies. The mutated Gαq/11 are perceived as oncogenic drivers in the vast majority of uveal melanoma (UM) cases, making directly targeting Gαq/11 to be a promising strategy for combating UM.
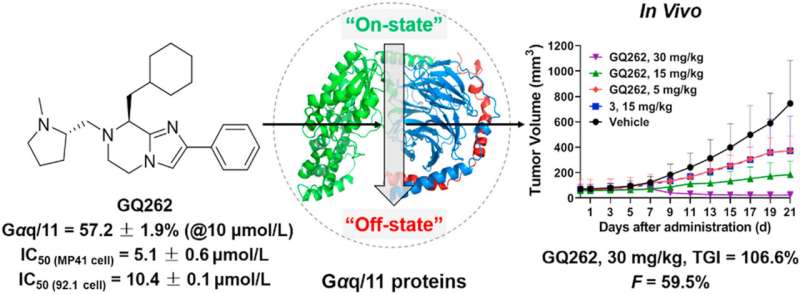
In this article, the authors report the optimization of imidazopiperazine derivatives as Gαq/11 inhibitors and identified GQ262 with improved Gαq/11 inhibitory activity and drug-like properties. GQ262 efficiently blocked UM cell proliferation and migration in vitro. Analysis of the apoptosis-related proteins, extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK), and yes-associated protein (YAP) demonstrated that GQ262 distinctly induced UM cells apoptosis and disrupted the downstream effectors by targeting Gαq/11 directly. Significantly, GQ262 showed outstanding antitumor efficacy in vivo with good safety at the testing dose.
These findings along with the favorable pharmacokinetics of GQ262 suggest that directly targeting Gαq/11 may be an efficient strategy against uveal melanoma.
The research was published in Acta Pharmaceutica Sinica B.
More information: Yang Ge et al, Discovery of small molecule Gαq/11 protein inhibitors against uveal melanoma, Acta Pharmaceutica Sinica B (2022). DOI: 10.1016/j.apsb.2022.04.016