Scientists reveal new TEV-mediated αPD-L1-specific therapy resistance mechanism
The immune checkpoint inhibitors, including anti-PD-1 and anti-PD-L1 antibodies (αPD-1 and αPD-L1), have revolutionized tumor immunotherapy. Although αPD-1 and αPD-L1 show excellent efficacy in various tumor types, even in patients with advanced tumors, only 10–30% of patients respond to αPD-1 and αPD-L1 therapy due to primary resistance.
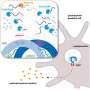
Extracellular vesicles (EVs) are highly involved in the progression of the tumor. PD-L1+ tumor-derived EVs (TEVs) cause systemic immunosuppression and possibly resist the αPD-L1 blockade. However, whether and how PD-L1+ TEVs mediate αPD-L1-therapy resistance remains unknown.
Recently, the research team led by Prof. Cai Zhijian from the Zhejiang University School of Medicine published an article entitled "Tumor extracellular vesicles mediate anti-PD-L1-therapy resistance by decoying anti-PD-L1" in Cellular & Molecular Immunology. The findings reveal a new TEV-mediated αPD-L1-specific therapy resistance mechanism, thus providing promising strategies to improve αPD-L1 efficacy.
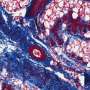
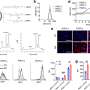
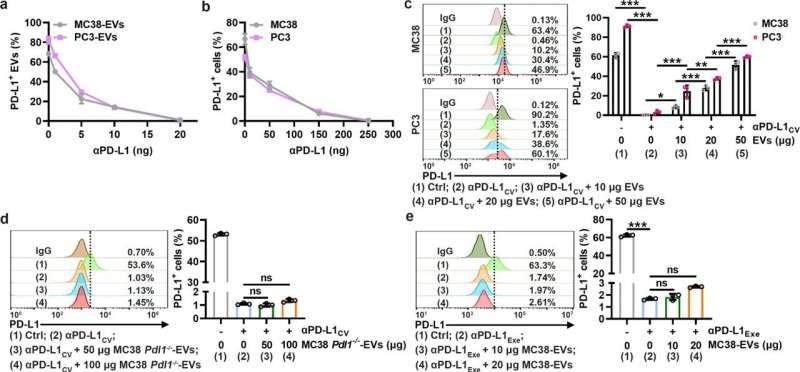
In this study, researchers found that TEVs could bind to αPD-L1 and compete with tumor cells through PD-L1 in vitro. Subsequently, the authors visualized αPD-L1 and tumor PD-L1 interactions as a red fluorescent spot detected by a proximity ligation assay (PLA). The PLA spots on tumor tissues were obviously reduced by injection of MC38-EVs but not MC38 Pdl1-/--EVs, while the PLA spots in tumor tissues significantly increased through inhibiting the secretion of endogenous EVs by knocking out Rab27a.
Furthermore, it was found that after binding TEVs, αPD-L1 is more taken up by phagocytes in the liver and spleen, leading to accelerated degradation and decreased tumor delivery of αPD-L1. In addition, they found that depletion of macrophages by Pexidartinib (PLX3397), which markedly reduced the numbers of peripheral monocytes and liver macrophages, eliminated αPD-L1-therapy resistance in TRAMP-C2-bearing mice.
These results demonstrate that targeting macrophages effectively prevents the clearance of TEV-bound αPD-L1, thus improving the utilization efficiency and therapy resistance of αPD-L1.
"In tumor tissue, due to the high-pressure environment, fewer antibodies could infiltrate into the depth of the tumor tissues. At the same time, these antibodies could be quickly captured by a large number of TEVs. Therefore, the consumption of αPD-L1 mediated by TEVs needs to be paid more attention in clinical therapy," said Prof. Cai.
More information: Jiming Chen et al, Tumor extracellular vesicles mediate anti-PD-L1 therapy resistance by decoying anti-PD-L1, Cellular & Molecular Immunology (2022). DOI: 10.1038/s41423-022-00926-6