Individuals with schizophrenia and social anhedonia show altered neural processing for social reward anticipation
Patients with schizophrenia and individuals with social anhedonia have been shown to exhibit impaired social reward processing that ultimately leads to impaired social interaction and social dysfunctions.
However, most of the previous studies on social reward anticipation in schizophrenia spectrum disorders were limited to behavioral design. It remains unclear whether the putative neural processing for social reward anticipation has been altered in both individuals with schizophrenia and individuals with social anhedonia.
Recently, a research team led by Dr. Raymond Chan from the Institute of Psychology (IP) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS) have conducted a study to specifically examine the underlying neural mechanisms of social reward anticipation in these populations.
The study was published in European Archives of Psychiatry and Clinical Neuroscience on Oct. 28.
The researchers recruited 23 individuals with schizophrenia and 17 healthy controls, as well as 37 individuals with social anhedonia and 50 healthy controls to complete the social incentive delay imaging task while they were undertaking MRI brain scans.
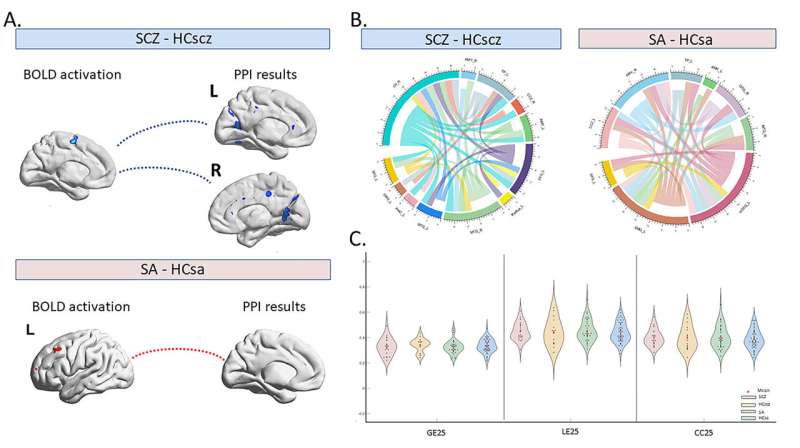
They found that individuals with schizophrenia exhibited hypo-activation of the left medial frontal gyrus and the negative functional connectivities (FCs) with the left parietal regions. However, individuals with social anhedonia exhibited the hyper-activation of the left middle frontal gyrus when anticipating social reward. Moreover, individuals with schizophrenia showed strengthened cerebellum-temporal FCs, whilst social anhedonia individuals showed strengthened FCs in left frontal regions.
These findings suggest that both individuals with schizophrenia and with social anhedonia exhibit altered neural processing for social reward anticipation, and such neural activities show a weakened association with real-life social network characteristics.
The study advances our understanding on the neural underpinnings of social motivation in schizophrenia spectrum disorders.
More information: Yi-jing Zhang et al, Altered neural mechanism of social reward anticipation in individuals with schizophrenia and social anhedonia, European Archives of Psychiatry and Clinical Neuroscience (2022). DOI: 10.1007/s00406-022-01505-6