This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
proofread
Isoform-specific AMPK repression affects cognitive function in aged mice, researchers find
The Aging journal has published a new research paper titled Isoform-specific effects of neuronal repression of the AMPK catalytic subunit on cognitive function in aged mice.
AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) functions as a molecular sensor that plays a critical role in maintaining cellular energy homeostasis. Dysregulation of the AMPK signaling has been linked to synaptic failure and cognitive impairments. In a recent study, researchers Xueyan Zhou, Wenzhong Yang, Xin Wang, and Tao Ma from Wake Forest University School of Medicine demonstrated abnormally increased AMPK activity in the hippocampus of aged mice. The kinase catalytic subunit of AMPK exists in two isoforms, α1 and α2, and their specific roles in aging-related cognitive deficits are unknown.
"Taking advantage of the unique transgenic mice (AMPKα1/α2 cKO) recently developed by our group, we investigated how isoform-specific suppression of the neuronal AMPKα may contribute to the regulation of cognitive and synaptic function associated with aging," the researchers write.
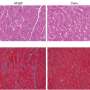
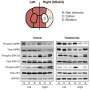
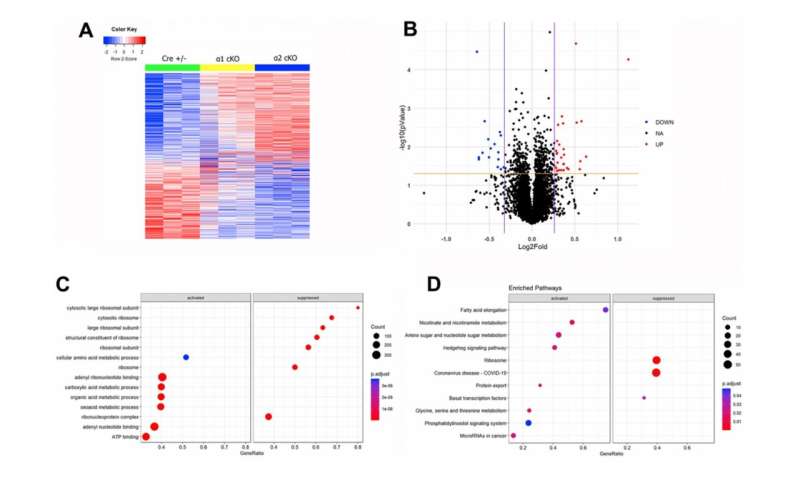
The team found that aging-related impairment of long-term object recognition memory was improved with suppression of AMPKα1 but not AMPKα2 isoform. Moreover, aging-related spatial memory deficits were unaltered with suppression of either AMPKα isoform. Biochemical experiments showed that the phosphorylation levels of the eukaryotic initiation factor 2 α subunit (eIF2α) were specifically decreased in the hippocampus of the AMPKα1 cKO mice. The team further performed large-scale unbiased proteomics analysis and revealed identities of proteins whose expression is differentially regulated with AMPKα isoform suppression. These novel findings may provide insights into the roles of AMPK signaling pathway in cognitive aging.
The researchers conclude, "In summary, the current study reported that suppression of neuronal AMPKα1 isoform can improve aging-related impairments of long-term recognition memory."
More information: Xueyan Zhou et al, Isoform-specific effects of neuronal repression of the AMPK catalytic subunit on cognitive function in aged mice, Aging (2023). DOI: 10.18632/aging.204554