This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
peer-reviewed publication
proofread
Key memory receptors are located on interneurons, finds study
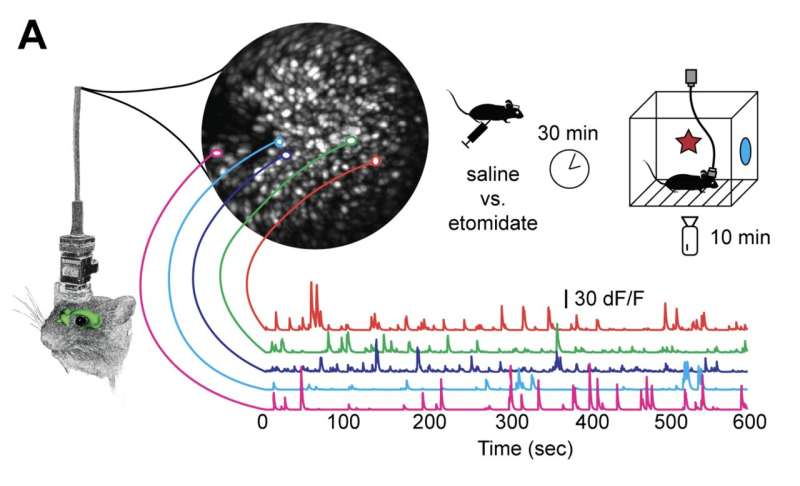
A key receptor regulating memory formation has been localized to interneurons, according to a study with implications for drug development.
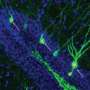
Robert Pearce and colleagues probed the localization of γ-aminobutyric acid type A receptors that incorporate α5 subunits (α5-GABAARs). α5-GABAARs are concentrated within the hippocampus, a brain structure that is essential for the formation of episodic memories. Their research is published in the journal PNAS Nexus.
The general anesthetic etomidate blocks learning by targeting α5-GABAARs, as do many drugs designed to enhance cognition, intended for use in people with Alzheimer's disease, Down syndrome, autism, depression, and schizophrenia.
Researchers have assumed that these drugs act through α5-GABAARs on pyramidal neurons, but by monitoring the formation and stability of spatial memories directly within the hippocampus of mice, the authors found that selectively knocking α5-GABAARs out of interneurons rendered etomidate ineffective in blocking memory formation and impaired spatial memory overall.
By contrast, knocking α5-GABAARs out of pyramidal neurons did not alter memory, and did not prevent etomidate from blocking spatial memories. The authors conclude that interneuronal α5-GABAARs serve a physiological role in promoting spatial learning, and serve as essential targets for etomidate modulation of contextual memory.
More information: Mengwen Zhu et al, Control of contextual memory through interneuronal α5-GABAA receptors, PNAS Nexus (2023). DOI: 10.1093/pnasnexus/pgad065