This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
proofread
Examining the long-term impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on health services utilization
The COVID-19 pandemic has a tremendous impact on health, daily life and the economy of the world on a global scale. It poses a great challenge to equity and accessibility of health services and the resilience of health care systems, especially in low and middle level developing countries.
It has been shown that the COVID-19 pandemic had different short-term impact on health status and health services; however, there has been few reports on the long-term impact.
This knowledge gap has prompted a team of researchers in China to evaluate the two-year long-term effect of the COVID-19 pandemic on health services utilization and the regional differences in the country.
Between Jan 2017 and Dec 2021, the team of researchers conducted a nationwide longitudinal study using routinely collected national data on health services utilization in the National Health Information System of China. They extracted national and provincial data of demographic characteristics, socio-economic characteristics, and health resources to evaluate the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on health services utilization in mainland China.
Min Liu, co-corresponding author of the study and professor at the Department of Epidemiology and Biostatistics, School of Public Health at Peking University in Beijing China, shared that their analysis included 34.2 billion health care facility visits and 1.1 billion discharged inpatients.
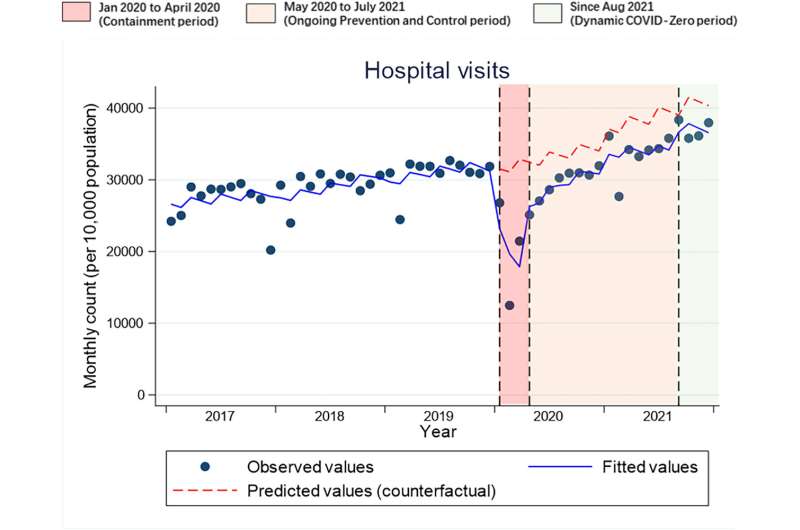
"The greatest impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on health care services utilization was observed during the containment period; there was a 32% reduction in hospital visits, 27% decrease for community health centers and 22% decline for township centers," explained Liu. "Over time, this effect on health care facility visits and discharged patients began to subside and eventually disappeared. Yet even two years later, there remained a negative impact on utilization rates of beds, length of stay, inpatient costs as well as average outpatient costs across different facilities."
Notably, this is the first large-scale study of the long-term impact of COVID-19 pandemic on health services. The team reported their findings, which highlighted the importance of maintaining primary health care services during the pandemic and strengthen resilient health system on the rapid recovery of health services during the pandemic, in the journal Global Transitions.
"We also found that there are disparities in the recovery of health services. Differences in terms of regions, socioeconomic statuses and facilities regarding the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic were also observed," added co-corresponding author Wanniang Liang, professor at Vanke School of Public Health, Tsinghua University, Beijing, China. "Providing people-centered health care, improving high-quality health care service delivery and strengthening the ability of primary health care institutions would help to increase the effectiveness and efficiency of health system during future pandemics."
More information: Jue Liu et al, Long-term impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on health services utilization in China: A nationwide longitudinal study, Global Transitions (2023). DOI: 10.1016/j.glt.2023.03.002