This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
trusted source
proofread
A meta-analysis of hybrid-closed loop control-IQ technology
A new study evaluated the effect of hybrid-closed loop Control-IQ technology in the pooled data from three randomized controlled trials, comparing Control-IQ to a control group using continuous glucose monitoring in people with type 1 diabetes. The study, which examined subgroup based on baseline characteristics such as race/ethnicity, socio-economic status, pre-study insulin delivery modality, and baseline glycemic control, is published in Diabetes Technology & Therapeutics.
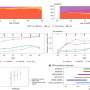
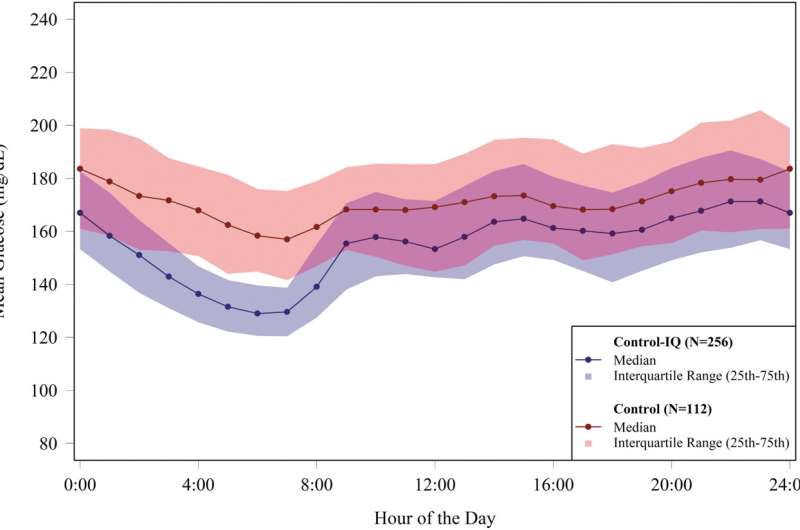
Roy W. Beck, MD, Ph.D., from the JAEB Center for Health Research, and coauthors, reported that time in range (70-180 mg/dL) in the Control-IQ group increased from 57%±17% at baseline to 70%±11% during follow up. In the control group the time in range was 56%±15% and 57%±14%, respectively. This represents an increase of 2.8 hours per day on average.
"Significant reductions in mean glucose, hyperglycemia metrics, hypoglycemic metrics and HbA1c also were observed," stated the investigators. "The greatest benefit was observed in participants with the worst baseline glycemic control in whom the auto-bolus feature of the Control-IQ algorithm appears to have substantial impact," they concluded.
Editor-in-Chief of Diabetes Technology & Therapeutics Satish Garg, MD, from the University of Colorado Denver, Barbara Davis Center for Childhood Diabetes, states, "Increasing improvements in diabetes technologies has improved glucose control as measured by Time-in-Range with a significant reduction in hypoglycemia as shown above."
More information: Roy W. Beck et al, A Meta-Analysis of Randomized Trial Outcomes for the t:slim X2 Insulin Pump with Control-IQ Technology in Youth and Adults from Age 2 to 72, Diabetes Technology & Therapeutics (2023). DOI: 10.1089/dia.2022.0558