This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
peer-reviewed publication
trusted source
proofread
New neurological target to help people walk again after a spinal cord injury
People who have lost control of their legs following a spinal cord injury may walk again someday. A research team affiliated with Université Laval and the CHU de Québec-Université Laval Research Center has pinpointed a new neurological target that could improve the recovery of gait.
Contrary to popular belief, spinal cord injuries are rarely complete. The brain retains access to the spinal cord circuitry below the lesion, but this connection is often dormant. Deep brain stimulation, or electrical stimulation, could activate it and promote recovery of locomotion. But which area of the brain should be targeted?
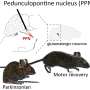
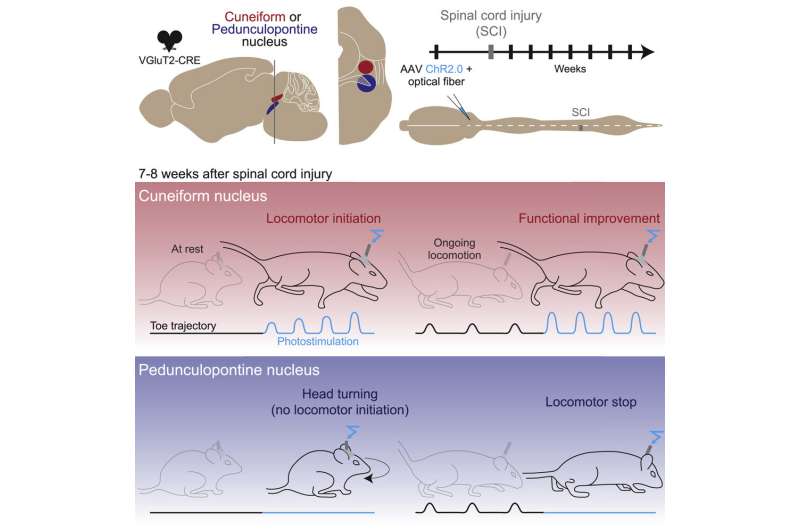
A research team led by Frédéric Bretzner, a professor at a professor at Université Laval's Faculty of Medicine, has focused on a locomotor center of the brain known as the mesencephalic locomotor region.
This area is known as a trigger and accelerator for walking in several animal species. It is composed of the cuneiform nucleus and the pedunculopontine nucleus. Deep brain stimulation of the pedunculopontine nucleus has generated ambiguous results in Parkinson's patients with gait and postural disorders. However, there are no clinical studies on the cuneiform nucleus.
A promising area of the brain
Professor Frédéric Bretzner's team used optogenetics to modify neurons to make them light-sensitive. The team then used blue light to activate glutamatergic, or excitatory, neurons in the cuneiform or pedunculopontine nucleus in mice.
"After spinal cord injury, stimulation in the cuneiform nucleus of excitatory neurons initiated walking in resting mice. During a spontaneous walking episode, stimulation also improved the quality of the mouse's walk and the coordination between the muscles of its hind legs," explains Frédéric Bretzner.
Conversely, the stimulation of glutamatergic neurons in the pedunculopontine nucleus rarely triggered walking in mice at rest. Stimulation even caused mice to stop when they walked.
"Our results suggest that the cuneiform nucleus would be a better neurological target than the pedunculopontine nucleus to improve walking recovery in people with a spinal cord injury," reports Professor Bretzner.
While waiting for the development of implants and optogenetic tools adapted to target glutamatergic neurons of the cuneiform nucleus in humans, electrical stimulation of the cuneiform nucleus could already improve walking recovery in patients with spinal cord injury.
This approach could also improve the quality of life of individuals suffering from traumas or neurodegenerative diseases affecting gait and posture, such as stroke, amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, or Parkinson's disease.
The findings are published in the journal Cell Reports Medicine.
More information: Marie Roussel et al, Functional contribution of mesencephalic locomotor region nuclei to locomotor recovery after spinal cord injury, Cell Reports Medicine (2023). DOI: 10.1016/j.xcrm.2023.100946