This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
peer-reviewed publication
trusted source
proofread
AI with volumetric thresholds facilitate opportunistic screening for splenomegaly
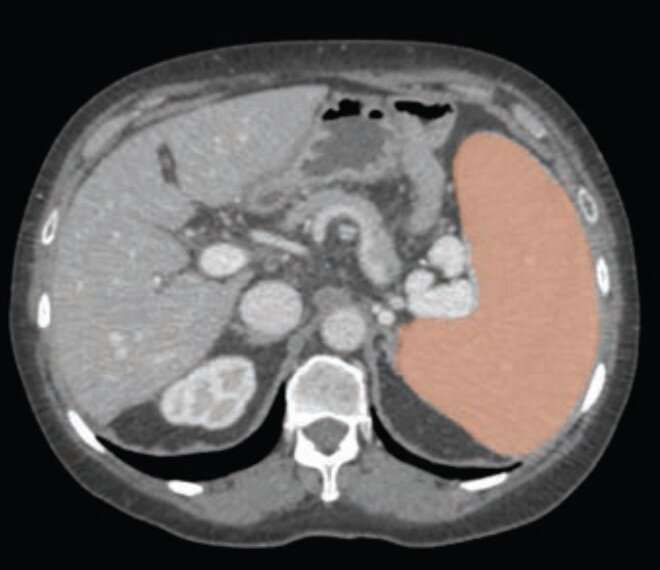
According to an accepted manuscript published in ARRS' own American Journal of Roentgenology (AJR), using an automated deep-learning AI tool, as well as weight-based volumetric thresholds, might afford large-scale evaluation for splenomegaly on CT examinations performed for any indication.
Noting that, historically, the standard linear splenic measurements used as a surrogate for splenic volume yielded suboptimal performance in detecting volume-based splenomegaly, "the weight-based volumetric thresholds indicated the presence of splenomegaly in most patients who underwent pre-liver transplant CT," explained corresponding author Perry J. Pickhardt, MD, from the department of radiology at University of Wisconsin School of Medicine & Public Health.
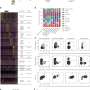
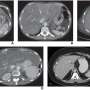
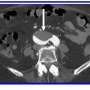
Pickhardt and colleagues' AJR accepted manuscript included a screening sample of 8,901 patients (4,235 men, 4,666 women; mean age, 56 years) who underwent CT colonoscopy (n = 7736) or renal-donor CT (n = 1165) from April 2004 to January 2017. A secondary cohort of 104 patients (62 men, 42 women; mean age, 56 years) with end-stage liver disease underwent pre-liver transplant CT from January 2011 to May 2013. Pickhardt et al.'s deep learning algorithm—previously developed, trained, and tested at the National Institutes of Health Clinical Center—was used for spleen segmentation, to help determine splenic volumes, with two radiologists independently reviewing a subset of said segmentations.
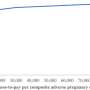
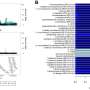
Ultimately, this automated deep-learning AI tool was utilized to calculate splenic volumes from CT examinations in 8,853 patients from the primary outpatient population. Additionally, splenic volume was most strongly associated with weight, among a range of patient factors.
"To our knowledge," the AJR authors concluded, "this study represents the largest reported sample of patients to undergo volumetric segmentation of the spleen."
More information: Alberto A. Perez et al, Automated Deep Learning Artificial Intelligence Tool for Spleen Segmentation on CT: Defining Volume-Based Thresholds for Splenomegaly, American Journal of Roentgenology (2023). DOI: 10.2214/AJR.23.29478